Discovery of Molidustat (BAY 85-3934): A Small-Molecule Oral HIF-Prolyl Hydroxylase (HIF-PH) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Renal Anemia
- PMID: 29485740
- PMCID: PMC6001664
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700783
Discovery of Molidustat (BAY 85-3934): A Small-Molecule Oral HIF-Prolyl Hydroxylase (HIF-PH) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Renal Anemia
Abstract
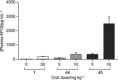
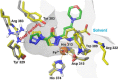
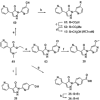
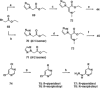
Small-molecule inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylases (HIF-PHs) are currently under clinical development as novel treatment options for chronic kidney disease (CKD) associated anemia. Inhibition of HIF-PH mimics hypoxia and leads to increased erythropoietin (EPO) expression and subsequently increased erythropoiesis. Herein we describe the discovery, synthesis, structure-activity relationship (SAR), and proposed binding mode of novel 2,4-diheteroaryl-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-ones as orally bioavailable HIF-PH inhibitors for the treatment of anemia. High-throughput screening of our corporate compound library identified BAY-908 as a promising hit. The lead optimization program then resulted in the identification of molidustat (BAY 85-3934), a novel small-molecule oral HIF-PH inhibitor. Molidustat is currently being investigated in clinical phase III trials as molidustat sodium for the treatment of anemia in patients with CKD.
Keywords: BAY 85-3934; HIF-PH; inhibitors; metalloenzymes; molidustat.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures



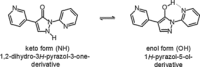



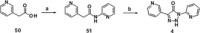

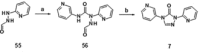

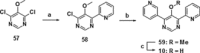



Similar articles
-
Mimicking hypoxia to treat anemia: HIF-stabilizer BAY 85-3934 (Molidustat) stimulates erythropoietin production without hypertensive effects.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e111838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111838. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25392999 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-man-proof of concept study with molidustat: a novel selective oral HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for the treatment of renal anaemia.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1557-1565. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13584. Epub 2018 May 14. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29575006 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The drug-specific properties of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in mice reveal a significant contribution of the kidney compared to the liver to erythropoietin induction.Life Sci. 2024 Jun 1;346:122641. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122641. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38614299
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: A Potential New Treatment for Anemia in Patients With CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2017 Jun;69(6):815-826. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28242135 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors: a paradigm shift for treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease?Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Aug;29(8):831-844. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1777276. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32476498 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors as a New Treatment Option for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 18;12(8):1884. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081884. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of oral iron and calcium supplement on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of molidustat: an oral HIF-PH inhibitor for the treatment of renal anaemia.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;76(2):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s00228-019-02813-y. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31919558 Clinical Trial.
-
Bidirectional modulation of HIF-2 activity through chemical ligands.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Apr;15(4):367-376. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0234-5. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 30804532 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs That Mimic Hypoxia Selectively Target EBV-Positive Gastric Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 19;15(6):1846. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061846. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980731 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylation protects from cyclophosphamide-induced bladder injury and urinary dysfunction.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jul 1;323(1):F81-F91. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00344.2021. Epub 2022 May 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35499237 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

