Efficacy of Tympanoplasty Without Mastoidectomy for Treating Chronic Otitis Media in Patients With Mastoid Cavity Opacification in Temporal Bone Computed Tomography Findings
- PMID: 29486541
- PMCID: PMC5831660
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2017.00878
Efficacy of Tympanoplasty Without Mastoidectomy for Treating Chronic Otitis Media in Patients With Mastoid Cavity Opacification in Temporal Bone Computed Tomography Findings
Abstract
Objectives: Combined mastoidectomy is generally preferred to tympanoplasty alone when treating patients with chronic otitis media (COM), particularly when temporal bone computed tomography (TBCT) shows that the mastoid cavity contains opacification of soft tissue density. However, in cases with Eustachian tube dysfunction, a mastoid cavity volume may be a burden to its function. We hypothesized that tympanoplasty alone might be better than tympanoplasty combined with mastoidectomy because soft tissue in the mastoid cavity is a sequel to a protective physiological response. Thus, we explored the efficacy of tympanoplasty without mastoidectomy in COM patients exhibiting mastoid air cell opacification on TBCT.
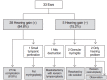
Methods: Between 2010 and 2014, a total of 33 patients, diagnosed with COM and with evidence of mastoid cavity opacification on TBCT, underwent tympanoplasty without mastoidectomy. All ears had been dry for ≥3 months before surgery. All procedures were performed by the same surgeon. We retrospectively analyzed the preoperative otoscopic findings, pre- and postoperative pure tone averages (PTAs; the mean of the values at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz), surgical procedures, and complications or recurrence.
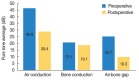
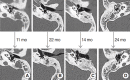
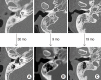
Results: Of the 33 patients, 28 (84.8%) exhibited hearing improvement after surgery. The mean pre- and postoperative PTAs were 46.9±21.2 dB and 29.4±17.0 dB, respectively (P<0.001). The air-bone gap decreased from 25.7±10.7 dB to 10.3±8.7 dB (P<0.001). Thirty-two patients (97.0%) did not develop any COM recurrence or cholesteatoma; one patient developed attic retraction of the tympanic membrane. Other minor complications were transient otorrhea caused by myringitis (two cases) and a pinpoint perforation (one case).
Conclusion: Tympanoplasty alone, i.e., without mastoidectomy, may adequately control COM, if it shows dry-up status for at least 3 months even though mastoid cavity opacification is detected in TBCT.
Keywords: Computed Tomography; Mastoidectomy; Otitis Media; Temporal Bone; Tympanoplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Brackmann DE, Shelton C, Arriaga MA. Otologic surgery. 1st ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 1994.
-
- Vartiainen E, Kansanen M. Tympanomastoidectomy for chronic otitis media without cholesteatoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992 Mar;106(3):230–4. - PubMed
-
- Mishiro Y, Sakagami M, Kondoh K, Kitahara T, Kakutani C. Long-term outcomes after tympanoplasty with and without mastoidectomy for perforated chronic otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009 Jun;266(6):819–22. - PubMed
-
- Webb BD, Chang CY. Efficacy of tympanoplasty without mastoidectomy for chronic suppurative otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Nov;134(11):1155–8. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly BJ, Chevretton EB, Wylie I, Thakkar C, Butler P, Sathanathan N, et al. The value of CT scanning in chronic suppurative otitis media. J Laryngol Otol. 1991 Dec;105(12):990–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

