Symmetry between repulsive and attractive interactions in driven-dissipative Bose-Hubbard systems
- PMID: 29487298
- PMCID: PMC5829241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21845-5
Symmetry between repulsive and attractive interactions in driven-dissipative Bose-Hubbard systems
Abstract
The driven-dissipative Bose-Hubbard model can be experimentally realized with either negative or positive onsite detunings, inter-site hopping energies, and onsite interaction energies. Here we use one-dimensional matrix product density operators to perform a fully quantum investigation of the dependence of the non-equilibrium steady states of this model on the signs of these parameters. Due to a symmetry in the Lindblad master equation, we find that simultaneously changing the sign of the interaction energies, hopping energies, and chemical potentials leaves the local boson number distribution and inter-site number correlations invariant, and the steady-state complex conjugated. This shows that all driven-dissipative phenomena of interacting bosons described by the Lindblad master equation, such as "fermionization" and "superbunching", can equivalently occur with attractive or repulsive interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
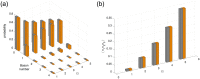
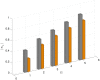

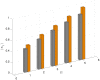
References
-
- Grujic T, Clark SR, Jaksch D, Angelakis DG. Repulsively induced photon superbunching in driven resonator arrays. Physical Review A. 2013;87:053846. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.87.053846. - DOI
-
- Biella A, Mazza L, Carusotto I, Rossini D, Fazio R. Photon transport in a dissipative chain of nonlinear cavities. Physical Review A. 2015;91:053815. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.91.053815. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

