Deep Learning for Computer Vision: A Brief Review
- PMID: 29487619
- PMCID: PMC5816885
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7068349
Deep Learning for Computer Vision: A Brief Review
Abstract
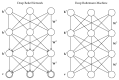
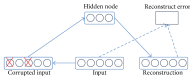
Over the last years deep learning methods have been shown to outperform previous state-of-the-art machine learning techniques in several fields, with computer vision being one of the most prominent cases. This review paper provides a brief overview of some of the most significant deep learning schemes used in computer vision problems, that is, Convolutional Neural Networks, Deep Boltzmann Machines and Deep Belief Networks, and Stacked Denoising Autoencoders. A brief account of their history, structure, advantages, and limitations is given, followed by a description of their applications in various computer vision tasks, such as object detection, face recognition, action and activity recognition, and human pose estimation. Finally, a brief overview is given of future directions in designing deep learning schemes for computer vision problems and the challenges involved therein.
Figures


References
-
- LeCun Y., Boser B., Denker J., et al. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In: Touretzky D., editor. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2 (NIPS∗89) Denver, CO, USA: 1990.
-
- TensorFlow, Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

