Monoclonal antibodies against metzincin targets
- PMID: 29488211
- PMCID: PMC6284333
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14186
Monoclonal antibodies against metzincin targets
Abstract
The metzincin clan of metalloproteinases includes the MMP, disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) and ADAM with thrombospondin motifs families, which cleave extracellular targets in a wide range of (patho)physiological processes. Antibodies constitute a powerful tool to modulate the activity of these enzymes for both therapeutic and research purposes. In this review, we give an overview of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that have been tested in preclinical disease models, human trials and important studies of metzincin structure and function. Initial attempts to develop therapeutic small molecule inhibitors against MMPs were hampered by structural similarities between metzincin active sites and, consequently, off-target effects. Therefore, more recently, mAbs have been developed that do not bind to the active site but bind to surface-exposed loops that are poorly conserved in closely related family members. Inhibition of protease activity by these mAbs occurs through a variety of mechanisms, including (i) barring access to the active site, (ii) disruption of exosite binding, and (iii) prevention of protease activation. These different modes of inhibition are discussed in the context of the antibodies' potency, selectivity and, importantly, the effects in models of disease and clinical trials. In addition, various innovative strategies that were used to generate anti-metzincin mAbs are discussed. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on Translating the Matrix. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v176.1/issuetoc.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
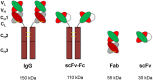
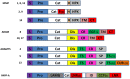
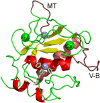
References
-
- Arroyo AG, Andrés V (2015). ADAMTS7 in cardiovascular disease: from bedside to bench and back again? Circulation 131: 1156–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

