Ghrelin for the management of cachexia associated with cancer
- PMID: 29489032
- PMCID: PMC6491219
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012229.pub2
Ghrelin for the management of cachexia associated with cancer
Abstract
Background: Cancer sufferers are amongst the most malnourished of all the patient groups. Studies have shown that ghrelin, a gut hormone can be a potential therapeutic agent for cachexia (wasting syndrome) associated with cancer. A variety of mechanisms of action of ghrelin in people with cancer cachexia have been proposed. However, safety and efficacy of ghrelin for cancer-associated cachexia have not been systematically reviewed. The aim of this review was to assess whether ghrelin is associated with better food intake, body composition and survival than other options for adults with cancer cachexia.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of ghrelin in improving food intake, body composition and survival in people with cachexia associated with cancer.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE and Embase without language restrictions up to July 2017. We also searched for ongoing studies in trials registers, performed handsearching, checked bibliographic references of relevant articles and contacted authors and experts in the field to seek potentially relevant research. We applied no restrictions on language, date, or publication status.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled (parallel-group or cross-over) trials comparing ghrelin (any formulation or route of administration) with placebo or an active comparator in adults (aged 18 years and over) who met any of the international criteria for cancer cachexia.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies for eligibility. Two review authors then extracted data and assessed the risk of bias for individual studies using standard Cochrane methodology. For dichotomous variables, we planned to calculate risk ratio with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and for continuous data, we planned to calculate mean differences (MD) with 95% CI. We assessed the evidence using GRADE and created 'Summary of findings' tables.
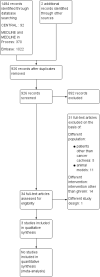
Main results: We screened 926 individual references and identified three studies that satisfied the inclusion criteria. Fifty-nine participants (37 men and 22 women) aged between 54 and 78 years were randomised initially, 47 participants completed the treatment. One study had a parallel design and two had a cross-over design. The studies included people with a variety of cancers and also differed in the dosage, route of administration, frequency and duration of treatment.One trial, which compared ghrelin with placebo, found that ghrelin improved food intake (very low-quality evidence) and had no adverse events (very low-quality evidence). Due to unavailability of data we were unable to report on comparisons for ghrelin versus no treatment or alternative experimental treatment modalities, or ghrelin in combination with other treatments or ghrelin analogues/ghrelin mimetics/ghrelin potentiators. Two studies compared a higher dose of ghrelin with a lower dose of ghrelin, however due to differences in study designs and great diversity in the treatment provided we did not pool the results. In both trials, food intake did not differ between participants on higher-dose and lower-dose ghrelin. None of the included studies assessed data on body weight. One study reported higher adverse events with a higher dose as compared to a lower dose of ghrelin.All studies were at high risk of attrition bias and bias for size of the study. Risk of bias in other domains was unclear or low.We rated the overall quality of the evidence for primary outcomes (food intake, body weight, adverse events) as very low. We downgraded the quality of the evidence due to lack of data, high or unclear risk of bias of the studies and small study size.
Authors' conclusions: There is insufficient evidence to be able to support or refute the use of ghrelin in people with cancer cachexia. Adequately powered randomised controlled trials focusing on evaluation of safety and efficacy of ghrelin in people with cancer cachexia is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Lundholm 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lundholm K, Gunnebo L, Körner U, Iresjö B-M, Engström C, Hyltander A, et al. Effects by daily long term provision of ghrelin to unselected weight-losing cancer patients: a randomized double-blind study. Cancer 2010;116(8):2044-52. - PubMed
Neary 2004 {published data only}
-
- Neary NM, Small CJ, Wren AM, Lee JL, Druce MR, Palmieri C, et al. Ghrelin increases energy intake in cancer patients with impaired appetite: acute, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2004;89(6):2832-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Strasser 2008 {published data only}
-
- Strasser F, Lutz T A, Maeder M T, Thuerlimann B, Bueche D, Tschöp M, et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of intravenous ghrelin for cancer-related anorexia/cachexia: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, double-crossover study. British Journal of Cancer 2008;98(2):300-8. - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adachi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Adachi S, Takiguchi S, Okada K, Yamamoto K, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, et al. Effects of ghrelin administration after total gastrectomy: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II study. Gastroenterology 2010;138(4):1312-20. - PubMed
Hiura 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hiura Y, Takiguchi S, Yamamoto K, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Yamasaki M, et al. Effects of ghrelin administration during chemotherapy with advanced esophageal cancer patients: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Cancer 2012;118(19):4785-94. - PubMed
NCT00933361 {published data only}
-
- NCT00933361. Individual dose-escalated bi-daily subcutaneously (sc) ghrelin in cancer cachexia: a Phase I/II Study. clinicaltrials.gov 2009. [NCT00933361]
Takata 2015 {published data only}
-
- Takata A, Takiguchi S, Miyazaki Y, Miyata H, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, et al. Randomized phase II study of the anti-inflammatory effect of ghrelin during the postoperative period of esophagectomy. Annals of Surgery 2015;262(2):230-6. - PubMed
Takiguchi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Takiguchi S, Hiura Y, Miyazaki Y, Takata A, Murakami K, Doki Y. Clinical trial of ghrelin synthesis administration for upper GI surgery. Methods in Enzymology 2012;514:409-31. - PubMed
Yamamoto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yamamoto K, Takiguchi S, Miyata H, Adachi S, Hiura Y, Yamasaki M, et al. Randomized phase II study of clinical effects of ghrelin after esophagectomy with gastric tube reconstruction. Surgery 2010;148(1):31-8. - PubMed
Additional references
Aapro 2014
-
- Aapro M, Arends J, Bozzetti F, Fearon K, Grunberg SM, Herrstedt J, et al. Early recognition of malnutrition and cachexia in the cancer patient: a position paper of a European School of Oncology Task Force. Annals of Oncology 2014;25(8):1492-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Akamizu 2010
Anderson 2017
-
- Anderson LJ, Albrecht ED, Garcia JM. Update on management of cancer-related cachexia. Current Oncology Reports 2017;19(1):3. - PubMed
Argilés 2013
-
- Argilés JM, Stemmler B. The potential of ghrelin in the treatment of cancer cachexia. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy 2013;13(1):67-76. - PubMed
Argilés 2017
AUREF 2012
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group. PaPaS Author and Referee Guidance. papas.cochrane.org/papas-documents (accessed on 16 August 2015).
Bai 2017
-
- Bai Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Yu X, Xu J, Hua Z, et al. Anamorelin for cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Supportive Care in Cancer 2017;25(5):1651-9. - PubMed
Baracos 2011
Bennani‐Baiti 2008
-
- Bennani-Baiti N, Davis MP. Cytokines and cancer anorexia cachexia syndrome. American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Care 2008;25(5):407-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bozzetti 2009
-
- Bozzetti F, Mariani L. Defining and classifying cancer cachexia: a proposal by the SCRINIO Working Group. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2009;33(4):361-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
CDC 2016
-
- Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL) | CDC. www.cdc.gov/hrqol/ May 2016.
Chen 2012
-
- Chen C-Y, Tsai C-Y. Ghrelin and motilin in the gastrointestinal system. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2012;18(31):4755-65. - PubMed
Chen 2015
Chen 2016
-
- Chen JL, Walton KL, Qian H, Colgan TD, Hagg A, Watt MJ, et al. Differential effects of IL6 and activin A in the development of cancer-associated cachexia. Cancer Research 2016;76(18):5372-82. - PubMed
Colldén 2017
Crawford 2015
-
- Crawford J. Cachexia. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2015;2:S158.
Cummings 2001
-
- Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001;50(8):1714-9. - PubMed
Cummings 2006
-
- Cummings David E. Ghrelin and the short- and long-term regulation of appetite and body weight. Physiology & Behavior 2006;89(1):71-84. - PubMed
Currow 2017
Date 2002
-
- Date Y, Murakami N, Toshinai K, Matsukura S, Niijima A, Matsuo H, et al. The role of the gastric afferent vagal nerve in ghrelin-induced feeding and growth hormone secretion in rats. Gastroenterology 2002;123(4):1120-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
DeBoer 2007
-
- DeBoer MD, Zhu X, Levasseur P, Meguid M, Suzuki S, Inui A, et al. Ghrelin treatment causes increased food intake and retention of lean body mass in a rat model of cancer cachexia. Endocrinology 2007;148(6):3004-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Dixit 2004
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta-analyses involving cross-over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Elmagarmid 2014
-
- Elmagarmid A, Fedorowicz Z, Hammady H, Ilyas I, Khabsa M, Ouzzani M. Rayyan: a systematic reviews web app for exploring and filtering searches for eligible studies for Cochrane Reviews [oral presentation]. In: Cochrane Colloquium. John Wiley & Sons, 2014.
Esposito 2015
-
- Esposito A, Criscitiello C, Gelao L, Pravettoni G, Locatelli M, Minchella I, et al. Mechanisms of anorexia-cachexia syndrome and rational for treatment with selective ghrelin receptor agonist. Cancer Treatment Reviews 2015;41(9):793-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Faulconbridge 2003
-
- Faulconbridge LF, Cummings DE, Kaplan JM, Grill HJ. Hyperphagic effects of brainstem ghrelin administration. Diabetes 2003;52(9):2260-5. - PubMed
Fearon 2006
-
- Fearon KC, Voss AC, Hustead DS. Definition of cancer cachexia: effect of weight loss, reduced food intake, and systemic inflammation on functional status and prognosis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;83(6):1345-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Fearon 2011
-
- Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncology 2011;12(5):489-95. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Fearon 2012
-
- Fearon KCH, Glass D, Guttridge DC. Cancer cachexia: mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell Metabolism 2012;16(2):153-66. - PubMed
Fujino 2003
Fujitsuka 2009
-
- Fujitsuka N, Asakawa A, Hayashi M, Sameshima M, Amitani H, Kojima S, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors modify physiological gastrointestinal motor activities via 5-HT2c receptor and acyl ghrelin. Biological Psychiatry 2009;65(9):748-59. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Fujitsuka 2011
Fujitsuka 2014
Fuoco 2015
-
- Fuoco D, Kilgour RD, Vigano A. A hypothesis for a possible synergy between ghrelin and exercise in patients with cachexia: biochemical and physiological bases. Medical Hypotheses 2015;85(6):927-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Garcia 2005
-
- Garcia JM, Garcia-Touza M, Hijazi RA, Taffet G, Epner D, Mann D, et al. Active ghrelin levels and active to total ghrelin ratio in cancer-induced cachexia. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2005;90(5):2920-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Garcia 2007
-
- Garcia J, Boccia R, Graham C, Kumor K, Polvino W. A phase II randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of RC-1291 (RC) for the treatment of cancer cachexia. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007 (June 20 Supplement);25(18S):9133.
Garcia 2009
-
- Garcia JM, Polvino WJ. Pharmacodynamic hormonal effects of anamorelin, a novel oral ghrelin mimetic and growth hormone secretagogue in healthy volunteers. Growth Hormone & IGF Research 2009;19(3):267-73. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Garcia 2013
-
- Garcia JM, Friend J, Allen S. Therapeutic potential of anamorelin, a novel, oral ghrelin mimetic, in patients with cancer-related cachexia: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, crossover, pilot study. Supportive Care in Cancer 2013;21(1):129-37. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Garcia 2015
-
- Garcia JM, Boccia RV, Graham CD, Yan Y, Duus EM, Allen S, et al. Anamorelin for patients with cancer cachexia: an integrated analysis of two phase 2, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials. Lancet Oncology 2015;16(1):108-16. [PMID: ] - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), (accessed on September 2015). Available at gradepro.org.
Gualillo 2001
-
- Gualillo O, Caminos J, Blanco M, Garcìa-Caballero T, Kojima M, Kangawa K, et al. Ghrelin, a novel placental-derived hormone. Endocrinology 2001;142(2):788-94. - PubMed
Guney 2007
-
- Guney Y, Ozel TU, Hicsonmez A, Nalca AM, Kurtman C. Ghrelin may reduce radiation-induced mucositis and anorexia in head-neck cancer. Medical Hypotheses 2007;68(3):538-40. - PubMed
Hatanaka 2015
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
ISRCTN26185223
-
- ISRCTN26185223. Randomised phase I/II - study with ghrelin versus placebo for patients with cancer-related anorexia/cachexia. ISRCTN registry 2005 (accessed 28 July 2017). [DOI: 10.1186/ISRCTN26185223] - DOI
Johns 2013
-
- Johns N, Stephens NA, Fearon KCH. Muscle wasting in cancer. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 2013;45(10):2215-29. - PubMed
Khatib 2014a
-
- Khatib MN, Gaidhane S, Gaidhane A, Syed ZQ. Role of ghrelin in regulation of growth hormone secretion by ghrelin-pituitary-GH axis. International Journal of Medical Science and Public Health 2014;3(4):425-9. [DOI: 10.5455/ijmsph.2014.250120141] - DOI
Khatib 2014b
Khatib 2014c
-
- Khatib MN, Khatib M, Gaidhane S, Gaidhane A, Quazi SZ. Ghrelin for regulating appetite and energy balance: a systematic review. National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2014;4(3):101-5. [DOI: 10.5455/njppp.2014.4.230420141] - DOI
Khatib 2014d
-
- Khatib MN, Gode D, Simkhada P, Agho K, Gaidhane S, Saxena D, et al. Somatotropic and cardio-protective effects of ghrelin in experimental models of heart failure: a systematic review. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2014;7(1):30-42. [DOI: 10.4103/1755-6783.145008] - DOI
Khatib 2014e
-
- Khatib MN, Gaidhane S, Simkhada P, Gaidhane A, Quazi SZ. Cardiovascular effects of ghrelin in heart failure: a systematic review. International Journal of Medical Science and Public Health 2014;3(6):756-63. [DOI: 10.5455/ijmsph.2014.060420141] - DOI
Khatib 2014f
Khatib 2015a
Khatib 2015b
Klok 2007
-
- Klok MD, Jakobsdottir S, Drent ML. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: a review. Obesity Reviews 2007;8(1):21-34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kojima 1999
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999;402(6762):656-60. - PubMed
Kojima 2008
-
- Kojima M, Kangawa K. Structure and function of ghrelin. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation 2008;46:89-115. - PubMed
Korbonits 2001
-
- Korbonits M, Bustin SA, Kojima M, Jordan S, Adams EF, Lowe DG, et al. The expression of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor ligand ghrelin in normal and abnormal human pituitary and other neuroendocrine tumors. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001;86(2):881-7. - PubMed
Kos 2009
-
- Kos K, Harte AL, O'Hare PJ, Kumar S, McTernan PG. Ghrelin and the differential regulation of des-acyl (DSG) and oct-anoyl ghrelin (OTG) in human adipose tissue (AT). Clinical Endocrinology 2009;70(3):383-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ledderose 2011
-
- Ledderose C, Kreth S, Beiras-Fernandez A. Ghrelin, a novel peptide hormone in the regulation of energy balance and cardiovascular function. Recent Patents on Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Drug Discovery 2011;5(1):1-6. - PubMed
Lin 2017
-
- Lin T-C, Hsiao M. Ghrelin and cancer progression. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 2017;1868(1):51-7. - PubMed
Loumaye 2017
-
- Loumaye A, Thissen J-P. Biomarkers of cancer cachexia. Clinical Biochemistry 2017;pii: S0009-9120(17):30427-7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.07.011. [Epub ahead of print]] - PubMed
Lucia 2012
-
- Lucia S, Esposito M, Rossi Fanelli F, Muscaritoli M. Cancer cachexia: from molecular mechanisms to patient's care. Critical Reviews in Oncogenesis 2012;17(3):315-21. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Madeddu 2015a
-
- Madeddu C, Mantovani G, Gramignano G, Astara G, Maccio A. Muscle wasting as main evidence of energy impairment in cancer cachexia: future therapeutic approaches. Future Oncology 2015;[Epub ahead of print]. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Madeddu 2015b
-
- Madeddu C, Mantovani G, Gramignano G, Maccio A. Advances in pharmacologic strategies for cancer cachexia. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2015;16(14):2163-77. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Masuda 2000
-
- Masuda Y, Tanaka T, Inomata N, Ohnuma N, Tanaka S, Itoh Z, et al. Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2000;276(3):905-8. - PubMed
Mendes 2015
-
- Mendes MCS, Pimentel GD, Costa FO, Carvalheira JBC. Molecular and neuroendocrine mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Journal of Endocrinology 2015;226(3):R29-43. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Molfino 2014
-
- Molfino A, Formiconi A, Rossi Fanelli F, Muscaritoli M. Ghrelin: from discovery to cancer cachexia therapy. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 2014;17(5):471-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mori 2000
-
- Mori K, Yoshimoto A, Takaya K, Hosoda K, Ariyasu H, Yahata K, et al. Kidney produces a novel acylated peptide, ghrelin. FEBS Letters 2000;486(3):213-6. - PubMed
Murphy 1998
-
- Murphy MG, Plunkett LM, Gertz BJ, He W, Wittreich J, Polvino WM, et al. MK-677, an orally active growth hormone secretagogue, reverses diet-induced catabolism. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1998;83(2):320-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Müller 2015
National Cancer Institute 2015
-
- National Cancer Institute, NIH. Cancer Trends Progress Report. progressreport.cancer.gov March 2015 (accessed 26 July 2017).
NCT00681486
-
- NCT00681486. Ghrelin - a possible opportunity to improve appetite (phase 3). ClinicalTrials.gov 2008. [NCT00681486 ]
Northrup 2013
Ohnuma 2017
-
- Ohnuma T, Adigun R. Cancer, Anorexia and Cachexia. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2017. - PubMed
Penna 2010
Penna 2016
Pietra 2014
Porporato 2013
Reid 2012
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ryan 2016
-
- Ryan AM, Power DG, Daly L, Cushen SJ, Ni Bhuachalla E, Prado CM. Cancer-associated malnutrition, cachexia and sarcopenia: the skeleton in the hospital closet 40 years later. In: Nutrition Society. 2016:1-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Sever 2016
Shin 2010
Stephens 2008
-
- Stephens NA, Skipworth RJ, Fearon KC. Cachexia, survival and the acute phase response. Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care 2008;2(4):267-74. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Stewart 2006
Sugiyama 2012
-
- Sugiyama M, Yamaki A, Furuya M, Inomata N, Minamitake Y, Ohsuye K, et al. Ghrelin improves body weight loss and skeletal muscle catabolism associated with angiotensin II-induced cachexia in mice. Regulatory Peptides 2012;178(1-3):21-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sun 2015
-
- Sun L, Quan XQ, Yu S. An epidemiological survey of cachexia in advanced cancer patients and analysis on its diagnostic and treatment status. Nutrition and Cancer 2015;67(7):1056-62. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2010
-
- Suzuki K, Simpson KA, Minnion JS, Shillito JC, Bloom SR. The role of gut hormones and the hypothalamus in appetite regulation. Endocrine Journal 2010;57(5):359-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Takeda 2008
-
- Takeda H, Sadakane C, Hattori T, Katsurada T, Ohkawara T, Nagai K, et al. Rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, suppresses cisplatin-induced anorexia in rats via 5-HT2 receptor antagonism. Gastroenterology 2008;134(7):2004-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Temel 2016
-
- Temel JS, Abernethy AP, Currow DC, Friend J, Duus EM, Yan Y, et al. Anamorelin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and cachexia (ROMANA 1 and ROMANA 2): results from two randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncology 2016;17(4):519-31. - PubMed
Teunissen 2007
-
- Teunissen SC, Wesker W, Kruitwagen C, De Haes HC, Voest EE, De Graeff A. Symptom prevalence in patients with incurable cancer: a systematic review. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2007;34(1):94-104. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tisdale 2009
-
- Tisdale MJ. Mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Physiological Reviews 2009;89(2):381-410. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tschop 2000
-
- Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000;407(6806):908-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tsubouchi 2014
-
- Tsubouchi H, Yanagi S, Miura A, Matsumoto N, Kangawa K, Nakazato M. Ghrelin relieves cancer cachexia associated with the development of lung adenocarcinoma in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 2014;743:1-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Utech 2012
Van der Lely 2004
-
- Van der Lely AJ, Tschöp M, Heiman ML, Ghigo E. Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocrine Reviews 2004;25(3):426-57. - PubMed
Velloso 2008
Volante 2002
-
- Volante M, Allìa E, Gugliotta P, Funaro A, Broglio F, Deghenghi R, et al. Expression of ghrelin and of the GH secretagogue receptor by pancreatic islet cells and related endocrine tumors. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2002;87(3):1300-8. - PubMed
von Haehling 2012
-
- Haehling S, Anker SD. Cachexia as major underestimated unmet medical need: facts and numbers. International Journal of Cardiology 2012;161(3):121-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Watanabe 1996
-
- Watanabe S, Bruera E. Anorexia and cachexia, asthenia, and lethargy. Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America 1996;10(1):189-206. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Windsor 1988
Wren 2001
-
- Wren AM, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Brynes AE, Frost GS, Murphy KG, et al. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001;86(12):5992. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2007
-
- Zhang W, Zhao L, Mulholland MW. Ghrelin stimulates myocyte development. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2007;20(5):659-64. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous