Mechanical properties of provisional dental materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29489883
- PMCID: PMC5830998
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193162
Mechanical properties of provisional dental materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Mechanical properties of provisional dental materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 17;13(4):e0196264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196264. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29664965 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Provisional restorations represent an important phase during the rehabilitation process, knowledge of the mechanical properties of the available materials allows us to predict their clinical performance. At present, there is no systematic review, which supports the clinicians' criteria, in the selection of a specific material over another for a particular clinical situation. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess and compare the mechanical properties of dimethacrylates and monomethacrylates used in fabricating direct provisional restorations, in terms of flexural strength, fracture toughness and hardness. This review followed the PRISMA guidelines. The searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Scopus, the New York Academy of Medicine Grey Literature Report and were complemented by hand-searching, with no limitation of time or language up to January 10, 2017. Studies that assess and compare the mechanical properties of dimethacrylate- and monomethacrylate-based provisional restoration materials were selected. A quality assessment of full-text articles were performed according to modified ARRIVE and CONSORT criteria and modified Cochrane Collaboration's tool for in vitro studies. Initially, 256 articles were identified. After removing the duplicates and applying the selection criteria, 24 articles were included in the qualitative synthesis and 7 were included in the quantitative synthesis (meta-analysis). It may be concluded that dimethacrylate-based provisional restorations presented better mechanical behavior than monomethacrylate-based ones in terms of flexural strength and hardness. Fracture toughness showed no significant differences. Within the monomethacrylate group, polymethylmethacrylate showed greater flexural strength than polyethylmethacrylate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


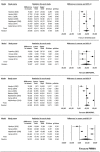
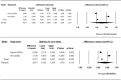

References
-
- Patras M, Naka O, Doukoudakis S, Pissiotis A. Management of provisional restorations’ deficiencies: A literature review. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2012;24: 26–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2011.00467.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kadiyala KK, Badisa MK, Anne G, Anche SC, Chiramana S, Muvva SB, et al. Evaluation of Flexural Strength of Thermocycled Interim Resin Materials Used in Prosthetic Rehabilitation- An In-vitro Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10: ZC91–ZC95. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/20020.8566 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burns DR, Beck DA, Nelson SK, Committee on Research in Fixed Prosthodontics of the Academy of Fixed Prosthodontics. A review of selected dental literature on contemporary provisional fixed prosthodontic treatment: report of the Committee on Research in Fixed Prosthodontics of the Academy of Fixed Prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;90: 474–97. - PubMed
-
- Urrútia G, Bonfill X. [PRISMA declaration: a proposal to improve the publication of systematic reviews and meta-analyses]. Med Clin (Barc). 2010;135: 507–11. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2010.01.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramamoorthi M, Bakkar M, Jordan J, Tran SD. Osteogenic Potential of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Preclinical Studies: A Systematic Review Using Modified ARRIVE and CONSORT Guidelines [Internet]. Stem Cells International. 2015. p. 378368 doi: 10.1155/2015/378368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

