It is time to apply biclustering: a comprehensive review of biclustering applications in biological and biomedical data
- PMID: 29490019
- PMCID: PMC6931057
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bby014
It is time to apply biclustering: a comprehensive review of biclustering applications in biological and biomedical data
Abstract
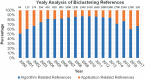
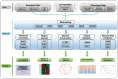
Biclustering is a powerful data mining technique that allows clustering of rows and columns, simultaneously, in a matrix-format data set. It was first applied to gene expression data in 2000, aiming to identify co-expressed genes under a subset of all the conditions/samples. During the past 17 years, tens of biclustering algorithms and tools have been developed to enhance the ability to make sense out of large data sets generated in the wake of high-throughput omics technologies. These algorithms and tools have been applied to a wide variety of data types, including but not limited to, genomes, transcriptomes, exomes, epigenomes, phenomes and pharmacogenomes. However, there is still a considerable gap between biclustering methodology development and comprehensive data interpretation, mainly because of the lack of knowledge for the selection of appropriate biclustering tools and further supporting computational techniques in specific studies. Here, we first deliver a brief introduction to the existing biclustering algorithms and tools in public domain, and then systematically summarize the basic applications of biclustering for biological data and more advanced applications of biclustering for biomedical data. This review will assist researchers to effectively analyze their big data and generate valuable biological knowledge and novel insights with higher efficiency.
Keywords: biclustering; biomarker and gene signatures detection; disease subtype identification; functional annotation; gene–drug association; modularity analysis; network elucidation.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- van Dijk EL, Auger H, Jaszczyszyn Y, et al.Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends Genet 2014;30(9):418–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

