Apatinib exhibits anti-leukemia activity in preclinical models of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 29490645
- PMCID: PMC5831852
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1421-y
Apatinib exhibits anti-leukemia activity in preclinical models of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Background: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a clonal malignant disorder characterized by an uncontrolled proliferation of immature B or T lymphocytes. Extensive studies have suggested an involvement of angiogenesis signaling in ALL progression and resistance to treatment. Thus, targeting angiogenesis with anti-angiogenic drugs may be a promising approach for ALL treatment. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of Apatinib, a novel receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor selectively targeting VEGFR-2 in ALL cells.
Method: ALL cell lines were treated with different concentration of Apatinib and then CCK8 assay, flow cytometry were used to determine the IC50 value and cell apoptosis, respectively. The effect of Apatinib against primary ALL cells from 11 adult patients and normal counterparts were also analyzed by apoptosis with flow cytometry. Next, we used western bolting and mass cytometry (CyTOF) assay to explore the underlying mechanism of the cytotoxicity of Apatinib. Finally, the anti-leukemia activity was further evaluated in an in vivo xenograft model of ALL.
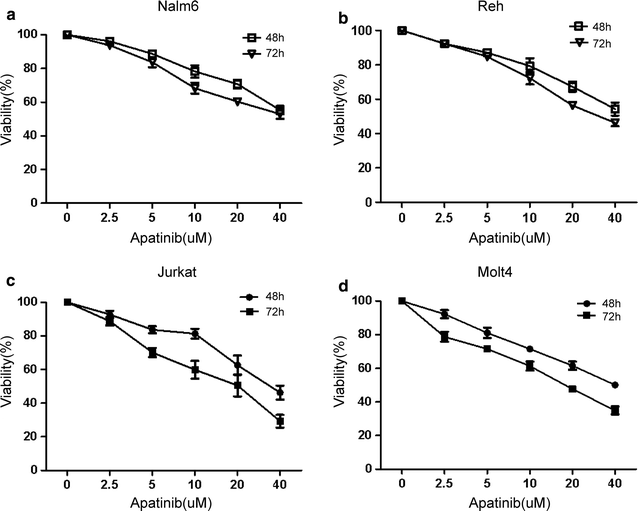
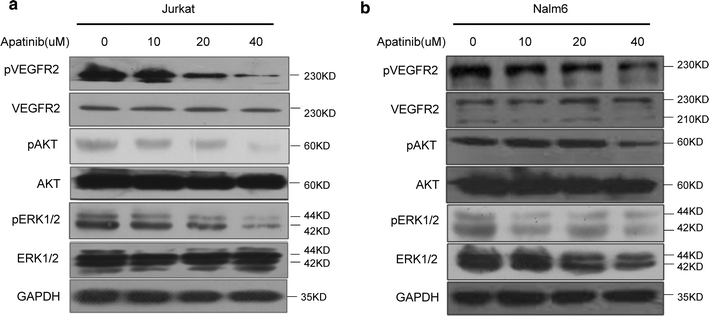
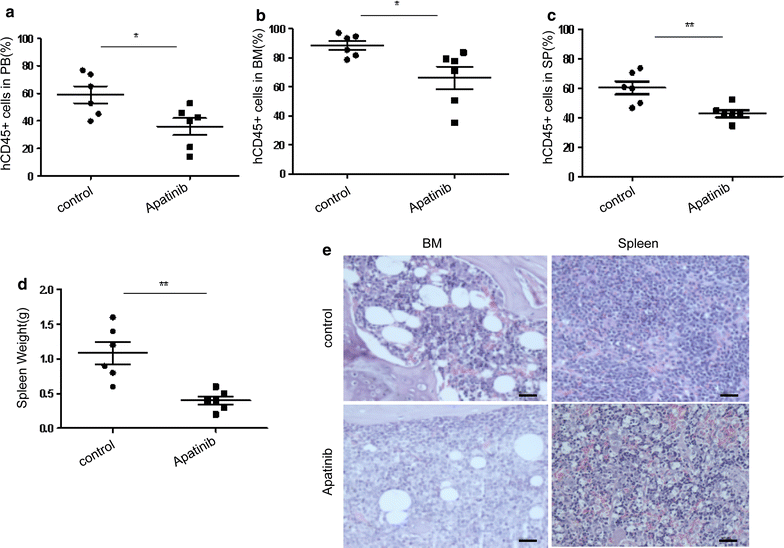
Results: Our results showed that Apatinib significantly inhibited cell growth and promoted apoptosis in both B and T lineage ALL cell lines in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The IC50 values of Apatinib against Nalm6, Reh, Jurkat and Molt4 for 48 h were 55.76 ± 13.19, 51.53 ± 10.74, 32.43 ± 5.58, 39.91 ± 9.88 μmol/L, and for 72 h were 30.34 ± 2.65, 31.96 ± 3.92, 17.62 ± 5.90, and 17.65 ± 2.17 μmol/L respectively. Similarly, Apatinib shows cytotoxic activity against primary adult ALL cells while sparing their normal counterparts in vitro. Moreover, Apatinib suppressed ALL growth and progression in an in vivo xenograft model. Mechanistically, Apatinib-induced cytotoxicity was closely associated with inhibition of VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling cascades, including the PI3 K, MAPK and STAT3 pathways.
Conclusion: Our study indicates that Apatinib exerts its anti-leukemia effect by inducing apoptosis through suppressing the VEGFR2 signaling pathway, supporting a potential role for Apatinib in the treatment of ALL.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Anti-angiogenic agent; Apatinib; Leukemia therapy; VEGFR2.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No.81570156/the National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81770126/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81700161/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2017J01354/Fujian Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2017-ZQN-83/The young and middle-aged talents training program of Fujian Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

