Foodborne Outbreak of Group G Streptococcal Pharyngitis in a School Dormitory in Osaka, Japan
- PMID: 29491014
- PMCID: PMC5925722
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01884-17
Foodborne Outbreak of Group G Streptococcal Pharyngitis in a School Dormitory in Osaka, Japan
Erratum in
-
Correction for Yamaguchi et al., "Foodborne Outbreak of Group G Streptococcal Pharyngitis in a School Dormitory in Osaka, Japan".J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Mar 28;57(4):e00090-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00090-19. Print 2019 Apr. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30923076 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
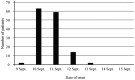
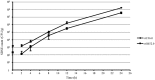
In September 2016, 140 patients with primary symptoms of sore throat and fever were identified in a school dormitory in Osaka, Japan. Epidemiological and laboratory investigations determined that these symptomatic conditions were from a foodborne outbreak of group G streptococcus (GGS), with GGS being isolated from samples from patients, cooks, and foods. The strain of GGS was identified as Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis of two emm types (stG652.0 and stC36.0). The causative food, a broccoli salad, was contaminated with the two types of S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, totaling 1.3 × 104 CFU/g. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) of samples from patients, cooks, and foods produced similar band patterns among samples with the same emm type. This result suggested the possibility of exposure from the contaminated food. The average onset time was 44.9 h and the prevalence rate was 62%. This is the first report to identify the causative food of a foodborne outbreak by Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis.
Keywords: foodborne outbreak; group G streptococcus.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical