Intracardiac Abscess and Pacemaker Lead Infection Secondary to Hematogenous Dissemination of Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus Aureus from a Prior Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Osteomyelitis
- PMID: 29491344
- PMCID: PMC5842747
- DOI: 10.12659/ajcr.906227
Intracardiac Abscess and Pacemaker Lead Infection Secondary to Hematogenous Dissemination of Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus Aureus from a Prior Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Osteomyelitis
Abstract
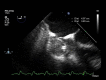
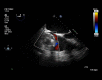
BACKGROUND Intracardiac abscesses are an unusual occurrence in developed countries. With the increase in use of implantable cardiac devices, the increase use of and advancements in antibiotics, and the longevity of patients with cardiac devices, one may expect an increase in such infections; however, case reports are rare. We are presenting a case in which hematogenous dissemination of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) infection from a lower extremity diabetic ulcer propagated into an infected pacemaker lead and ultimately an intracardiac abscess of the right atrium. CASE REPORT A 77-year-old male with a history of MSSA diabetic foot infection complicated by osteomyelitis presented with fever, syncope, and wide complex tachycardia, and he was found to have an intracardiac abscess and fibrinous lead vegetations. The patient was deemed too ill for invasive surgical intervention given his comorbidities, pacemaker generator replacement requirement, and intermittent ventricular tachycardia. The patient was subsequently sent home with oral antibiotics and home hospice per patient and family wishes. CONCLUSIONS This case demonstrated how hematogenous dissemination of MSSA infections from a diabetic foot ulcer and osteomyelitis can seed pacemaker hardware resulting in an intracardiac abscess. Unfortunately, our patient was too ill to undergo all procedures required to eradicate the abscess and infected pacemaker hardware. The standard of care would be complete hardware removal. Conservative management would include indefinite or prolonged antibiotic therapy, with the notion that intracardiac abscesses cannot be cured with antibiotics alone. This conservative management approach would be deemed necessary in a select population that cannot undergo surgical intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Case of Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Prostate Abscess, Osteomyelitis, and Myositis Associated with MSSA Bacteremia in a 60-Year-Old Patient Presenting with Back Pain.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Jul 2;23:e936704. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.936704. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35778821 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis with paravalvular abscess treated with daptomycin.Heart Lung. 2005 Jan-Feb;34(1):69-71. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2004.07.009. Heart Lung. 2005. PMID: 15647736
-
Cardiac device-related endocarditis complicated by spinal abscess.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012 Mar;35(3):269-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03288.x. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22150338
-
Pacemaker-induced Staphylococcus aureus mitral valve acute bacterial endocarditis complicated by persistent bacteremia from a coronary stent: Cure with prolonged/high-dose daptomycin without toxicity.Heart Lung. 2006 May-Jun;35(3):207-11. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2005.09.010. Heart Lung. 2006. PMID: 16701116 Review.
-
Serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Sep 15;51 Suppl 2:S183-97. doi: 10.1086/653519. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20731576 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute exacerbation of chronic osteomyelitis triggered by aggravation of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2019 Jan 7;13(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1954-y. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30621795 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Outpatient Treatment of Severe Diabetic-Foot Myositis and Osteomyelitis Caused by Extensively Drug-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis with Teicoplanin plus Rifampicin: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2023 Nov 1;24:e941337. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.941337. Am J Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37910441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernandez Guerrero ML, Gonzalez Lopez JJ, Goyenechea A, et al. Endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus: A reappraisal of the epidemiologic, clinical, and pathologic manifestations with analysis of factors determining outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 2009;88(1):1–22. - PubMed
-
- Lauridsen TK, Park L, Tong S, et al. Echocardiographic findings predict inhospital and one-year mortality in left-sided native valve Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: An analysis from the international collaboration on endocarditis-prospective echo cohort study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8(7):1–17. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

