Juvenile primary extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma, presenting as cheek swelling
- PMID: 29491611
- PMCID: PMC5824524
- DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_43_17
Juvenile primary extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma, presenting as cheek swelling
Abstract
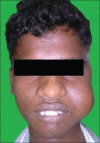
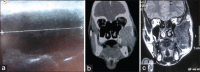
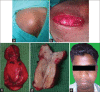
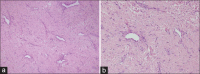
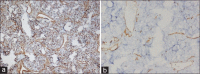
Angiofibroma is a locally advancing immensely vascular tumor that essentially arises from the nasopharynx. The clinical characteristics of extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma (ENA) do not accord to that of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma and can present a diagnostic confront. We describe a case of primary juvenile ENA in a 19-year-old patient who presented with a rapidly enlarging mass of the cheek region. The case is unusual because of its anatomic location. The diagnostic and management particulars are sketched.
Keywords: Cheek swelling; extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma; masticator space; vascular tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diode Laser Management of Primary Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Presenting as Maxillary Epulis: Report of a Case and Literature Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Jan 1;9(1):33. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9010033. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33401498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma of the ethmoid sinus: a distinct clinical entity at an unusual site.Ear Nose Throat J. 2012 Feb;91(2):E15-7. doi: 10.1177/014556131209100217. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012. PMID: 22359139
-
Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Localized in the Nasal Dorsum: A Rare Location for This Tumor.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018 Sep 28;52(3):229-231. doi: 10.5350/SEMB.20170508042536. eCollection 2018. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018. PMID: 32595404 Free PMC article.
-
Extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma: clinical and radiological presentation.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Feb;270(2):655-60. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-2041-4. Epub 2012 May 15. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 22584751 Free PMC article.
-
Extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma of the cheek.J Laryngol Otol. 2006 Feb;120(2):141-4. doi: 10.1017/S0022215105004573. Epub 2005 Dec 19. J Laryngol Otol. 2006. PMID: 16359575 Review.
Cited by
-
Diode Laser Management of Primary Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Presenting as Maxillary Epulis: Report of a Case and Literature Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Jan 1;9(1):33. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9010033. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33401498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Witt TR, Shah JP, Sternberg SS. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. A 30 year clinical review. Am J Surg. 1983;146:521–5. - PubMed
-
- Windfuhr JP, Remmert S. Extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma: Etiology, incidence and management. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004;124:880–9. - PubMed
-
- Chauveau UC. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Arch Int Laryng. 1906;21:889.
-
- McDaniel RK, Houston GD. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma with lateral extension into the cheek: Report of case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;53:473–6. - PubMed
-
- Neel HB 3rd, Whicker JH, Devine KD, Weiland LH. Juvenile angiofibroma. Review of 120 cases. Am J Surg. 1973;126:547–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

