Effectiveness of Test-Enhanced Learning (TEL) in lectures for undergraduate medical students
- PMID: 29492055
- PMCID: PMC5768821
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.336.13358
Effectiveness of Test-Enhanced Learning (TEL) in lectures for undergraduate medical students
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effectiveness of Test-Enhanced learning as a learning tool in lectures for undergraduate medical students.
Method: This quantitative, randomized controlled trial included eighty-four students of 4th year MBBS from Yusra Medical & Dental College, Islamabad. The duration of study was from March 2016 to August 2016. After obtaining the informed consent; participants were equally assigned to interventional and non-interventional study groups through stratified randomization. Single best answer MCQs of special pathology were used as data collection instrument after validation. A pre- and post-test was taken from both groups, before and after the intervention, respectively and their results were compared using SPSS version 21.
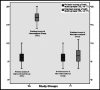
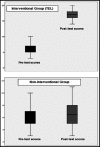
Results: There were 13 male (31%) and 29 female (69%) participants in each study group who showed an equivalent baseline performance on pre-test (p=0.95). Statistically significant difference was found among mean scores of interventional and non-interventional study groups at exit exam (p=0.00). Interventional group also showed a significant improvement in their post-test scores (mean: 17.17±1.59) as compared to pre-test scores (mean: 6.19±1.81).
Conclusions: Test-enhanced learning has significant effect on improving the learning of course content delivered to undergraduate medical students through lectures.
Keywords: Learning; Medical education; Medical students; Test-enhanced learning; Testing effect; Undergraduate lectures.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Ilic D, Maloney S. Methods of teaching medical trainees evidence-based medicine:a systematic review. Med Educ. 2014;48(2):124–135. doi:10.1111/medu.12288. - PubMed
-
- Christopher DA. Interactive large classes:The dynamics of teacher/student interaction. J Bus Econ Res. 2011;1(8)
-
- Prober CG, Heath C. Lecture halls without lectures—a proposal for medical education. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(18):1657–1659. doi:10.1056/nejmp1202451. - PubMed
-
- Richardson D. Don't dump the didactic lecture;fix it. Adv Physiol Educ. 2008;32(1):23–24. doi:10.1152/advan.00048.2007. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical