Circulating antithyroid antibodies contribute to the decrease of glomerular filtration rate in lithium-treated patients: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 29492700
- PMCID: PMC6161986
- DOI: 10.1186/s40345-017-0114-4
Circulating antithyroid antibodies contribute to the decrease of glomerular filtration rate in lithium-treated patients: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Concerns about the adverse effects of long-term treatment with lithium include reduced renal function. In the present study, we examined comorbidities which may be associated with chronic kidney disease in a cohort of patients treated with lithium for up to 41 years.
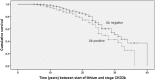
Methods: We studied 394 patients who were treated with lithium for ≥ 5 years. The potential role of comorbidities (diabetes, concurrent antihypertensive medication, treatment with L-thyroxine, and presence of antithyroid peroxidase/microsomes, anti-thyroglobulin, and/or anti-thyrotropin-receptor antibodies) was analysed. We focused on the categories of patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) lower than 60 or 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 as calculated from serum creatinine according to the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. We applied multivariate regression analysis and Cox survival analysis to study the effects exerted by sex, age, duration of lithium treatment, and comorbidities using eGFR categories as the dependent variable. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated to measure the time to decline to an eGFR lower than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 in patients with positive or negative thyroid antibodies.
Results: Age was associated with a decline to an eGFR lower than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 after controlling for sex, duration of lithium treatment, and comorbidities. Circulating thyroid antibodies were associated with a decline to an eGFR lower than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Conclusions: The present study is the first to suggest a potential role of circulating thyroid antibodies in the severe decline of eGFR in lithium-treated patients.
Keywords: Anti-thyroglobulin; Chronic; Glomerular filtration rate; Lithium; Renal insufficiency; Thyroid microsomal antibodies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal function during long-term lithium treatment: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study.BMC Med. 2015 Jan 21;13:12. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0249-4. BMC Med. 2015. PMID: 25604586 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effect of lithium maintenance therapy on estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with affective disorders: a population-based cohort study.Lancet Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;2(12):1075-83. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00316-8. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26453408
-
Duration of lithium treatment is a risk factor for reduced glomerular function: a cross-sectional study.BMC Med. 2013 Feb 11;11:33. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-33. BMC Med. 2013. PMID: 23399351 Free PMC article.
-
Key questions on the long term renal effects of lithium: a review of pertinent data.Int J Bipolar Disord. 2023 Nov 16;11(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40345-023-00316-5. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2023. PMID: 37971552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney, thyroid and other organ functions after 40 years or more of lithium therapy: a case series of five patients.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016 Aug;6(4):277-82. doi: 10.1177/2045125316643299. Epub 2016 Apr 17. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27536347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal function at follow-up in a cohort of patients who had shown reduced glomerular filtration rate during long-term treatment with lithium.J Nephrol. 2023 May;36(4):1079-1081. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01490-y. Epub 2022 Nov 9. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36350561 No abstract available.
-
Association between High Normal TSH Levels and Obesity in Women with Anti-Thyroid Autoantibodies (ATAs).J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 31;11(17):5125. doi: 10.3390/jcm11175125. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36079055 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical use of lithium salts: guide for users and prescribers.Int J Bipolar Disord. 2019 Jul 22;7(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40345-019-0151-2. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2019. PMID: 31328245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychotropic Drugs and Adverse Kidney Effects: A Systematic Review of the Past Decade of Research.CNS Drugs. 2022 Oct;36(10):1049-1077. doi: 10.1007/s40263-022-00952-y. Epub 2022 Sep 26. CNS Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36161425
-
Thyroid autoimmunity and hypothyroidism are associated with deep molecular response in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia on tyrosine kinase inhibitors.J Endocrinol Invest. 2022 Feb;45(2):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01613-5. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022. PMID: 34283388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldessarini RJ. Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders: depression and mania. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 9. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1996. pp. 431–459.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous