Taurine alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis
- PMID: 29494284
- PMCID: PMC6748701
- DOI: 10.1080/13510002.2018.1445581
Taurine alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis
Abstract
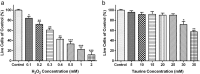
Osteoarthritis (OA), characterized by pain and stiffness, swelling, deformity and dysfunction of joints, affects large numbers of population. The purpose of this study was to discover the effects of taurine in human OA chondrocytes and explore the underlying mechanisms. 46 patients with different grades of OA were recruited. Of these patients, 24 underwent total knee replacement and cartilages were harvested. The mRNA expressions of type II collagen (Collagen II) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers (GRP78, GADD153 and Caspase-12) in cartilages were quantified by qRT-PCR. Cell viability and apoptosis of patient-derived chondrocytes were assessed by the CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry assay, respectively. Meanwhile, protein levels of Collagen II and ER stress markers both in cartilages and chondrocytes were evaluated by Western blot. The mRNA and protein levels of Collagen II decreased as OA progressed, while the expressions of ER stress markers increased dramatically. H2O2 induced ER stress in chondrocytes, as shown by the significant increase in the expression of ER stress markers, inhibited chondrocyte viability and Collagen II synthesis, promoted apoptosis. However, taurine treatment inhibited these above phenomena. These results indicated that taurine exhibited anti-OA effect by alleviating H2O2 induced ER stress and subsequently inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis.
Keywords: ER stress; H2O2; Taurine; anti-apoptosis; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
