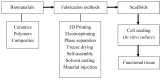
Recent Advances in Biomaterials for 3D Printing and Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 29494503
- PMCID: PMC5872108
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb9010022
Recent Advances in Biomaterials for 3D Printing and Tissue Engineering
Abstract
Three-dimensional printing has significant potential as a fabrication method in creating scaffolds for tissue engineering. The applications of 3D printing in the field of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering are limited by the variety of biomaterials that can be used in this technology. Many researchers have developed novel biomaterials and compositions to enable their use in 3D printing methods. The advantages of fabricating scaffolds using 3D printing are numerous, including the ability to create complex geometries, porosities, co-culture of multiple cells, and incorporate growth factors. In this review, recently-developed biomaterials for different tissues are discussed. Biomaterials used in 3D printing are categorized into ceramics, polymers, and composites. Due to the nature of 3D printing methods, most of the ceramics are combined with polymers to enhance their printability. Polymer-based biomaterials are 3D printed mostly using extrusion-based printing and have a broader range of applications in regenerative medicine. The goal of tissue engineering is to fabricate functional and viable organs and, to achieve this, multiple biomaterials and fabrication methods need to be researched.
Keywords: additive manufacturing; bioinks; biomaterials; bioprinting; ceramics; composites; polymers; three-dimensional printing; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interests is declared.
Figures
References
-
- Nair L.S., Laurencin C.T. Polymers as biomaterials for tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2006;102:47–90. - PubMed
-
- Badylak S. Principles of Regenerative Medicine. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2008. Naturally Occuring Scaffold Materials; pp. 594–603.
-
- Hacker M.C., Mikos A.G. Principles of Regenerative Medicine. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2008. Synthetic Polymers; pp. 604–635.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources