Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation
- PMID: 29494548
- PMCID: PMC5877566
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030705
Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation
Abstract
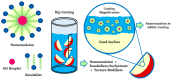
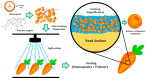
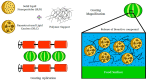
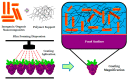
Currently, nanotechnology represents an important tool and an efficient option for extending the shelf life of foods. Reducing particle size to nanometric scale gives materials distinct and improved properties compared to larger systems. For food applications, this technology allows the incorporation of hydrophilic and lipophilic substances with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that can be released during storage periods to increase the shelf life of diverse products, including whole and fresh-cut fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, and cheese, among others. Edible coatings are usually prepared with natural polymers that are non-toxic, economical, and readily available. Nanosystems, in contrast, may also be prepared with biodegradable synthetic polymers, and liquid and solid lipids at room temperature. In this review, recent developments in the use of such nanosystems as nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanocomposites, and nanoemulsions, are discussed critically. The use of polymers as the support matrix for nanodispersions to form edible coatings for food preservation is also analyzed, but the central purpose of the article is to describe available information on nanosystems and their use in different food substrates to help formulators in their work.
Keywords: active compounds; biopolymers; essential oils; nanostructures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yousuf B., Qadri O.S., Srivastava A.K. Recent developments in shelf-life extension of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables by application of different edible coatings: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018;89:198–209. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.10.051. - DOI
-
- Wu Y., Luo Y., Wang Q. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of essential oils encapsulated in zein nanoparticles prepared by liquid–liquid dispersion method. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012;48:283–290. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2012.03.027. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

