Non-Native Conformational Isomers of the Catalytic Domain of PCSK9 Induce an Immune Response, Reduce Lipids and Increase LDL Receptor Levels
- PMID: 29495280
- PMCID: PMC5855862
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020640
Non-Native Conformational Isomers of the Catalytic Domain of PCSK9 Induce an Immune Response, Reduce Lipids and Increase LDL Receptor Levels
Abstract
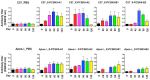
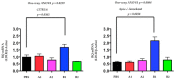
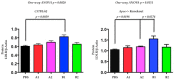
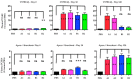
PCSK9 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) increases plasma cholesterol levels by promoting LDL receptor degradation. Current antibody inhibitors block the interaction between PCSK9 and LDL receptors, significantly decrease plasma cholesterol levels, and provide beneficial clinical outcomes. To reduce the action of PCSK9 in plasma, a novel strategy that will produce a panel of non-native, conformationally-altered isomers of PCSK9 (X-PCSK9) to develop active immunotherapy targeting of native PCSK9 and inhibiting/blocking the interaction of PCSK9 with LDL receptor, thus decreasing plasma cholesterol levels is proposed. The authors used the scrambled disulfide bond technique to generate conformationally-altered isomers of the catalytic domain of mouse PCSK9. The focus was on the immune response of four X-isomers and their effects on plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels in both C57BL/6J and Apoe-/- mice. The authors showed that the four immunogens produced significant immunogenicity against native PCSK9 to day 120 after immunization of C57BL/6J and Apoe-/- mice. This resulted in significantly decreased plasma cholesterol levels in C57BL/6J mice, and to a lesser degree in Apoe-/- mice. The X-PCSK9-B1 treated mice had increased LDL receptor mRNA and protein levels at day 120 after treatment. Thus, this study provides a new, potentially promising approach that uses long-term immunotherapy for a treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: LDL receptor; PCSK9; cholesterol; scrambled disulfide bonds; triglyceride.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Single Domain Antibodies Are Potent Inhibitors of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Degradation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16659-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.717736. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27284008 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Adiponectin Receptor Regulates Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Expression and Inhibits Lesions in ApoE-Deficient Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jul;37(7):1290-1300. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309630. Epub 2017 May 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28546220
-
LDL-R promoting activity of peptides derived from human PCSK9 catalytic domain (153-421): design, synthesis and biochemical evaluation.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Mar 6;92:890-907. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.022. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25679794
-
[PCSK9: Structure and function. PCSK9 and low-density lipoprotein receptor. Mutations and their effects].Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2016 May;28 Suppl 2:3-8. doi: 10.1016/S0214-9168(16)30164-4. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2016. PMID: 27888903 Review. Spanish.
-
Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.056. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23973703 Review.
Cited by
-
New Perspectives on Cholesterol and Lipoprotein Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 11;24(14):11298. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411298. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511058 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling Protein 2 Drives Myocardial Dysfunction in Murine Models of Septic Shock.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 4;2019:9786101. doi: 10.1155/2019/9786101. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31080837 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

