Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB
- PMID: 29495390
- PMCID: PMC6017010
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23030517
Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB
Abstract
Numerous herbal-derived natural products are excellent anti-inflammatory agents. Several studies have reported that aloin, the major anthraquinone glycoside obtained from the Aloe species, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity. However, the molecular mechanism of this activity is not well understood. In this report, we found that aloin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and nitric oxide production, and downregulates the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Aloin inhibits the phosphorylation and acetylation of the NF-κB p65 subunit by suppressing the upstream kinases p38 and Msk1, preventing LPS-induced p65 translocation to the nucleus. We have also shown that aloin inhibits LPS-induced caspase-3 activation and apoptotic cell death. Collectively, these findings suggest that aloin effectively suppresses the inflammatory response, primarily through the inhibition of NF-κB signaling.
Keywords: NF-κB; aloin; apoptosis; inflammation; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
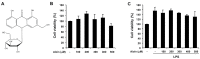





References
-
- Tomita T., Takeuchi E., Tomita N., Morishita R., Kaneko M., Yamamoto K., Nakase T., Seki H., Kato K., Kaneda Y., et al. Suppressed Severity of Collagen-Induced Arthritis by in Vivo Transfection of Nuclear Factor kappaB Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotides as a Gene Therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1999;42:2532–2542. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199912)42:12<2532::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

