Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor
- PMID: 29495408
- PMCID: PMC5876701
- DOI: 10.3390/s18030691
Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor
Abstract
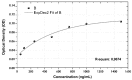
This study describes the development of an immunosensory label-free quantification methodology based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and its applicability in measuring/evaluating therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody (adalimumab) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The experimental parameters evaluated in this study were immobilising ligands by pre-concentration assays, sensor surface regeneration, ascertaining the method's sensitivity and correlating the results from quantifying plasma samples by ELISA immunoassay. The results showed that TNF-α quantification values (in RU) were significantly different when comparing patients (~50-250 RU) to controls (~10-20 RU). Likewise, there was 0.97 correlation for patients and 0.91 for healthy volunteers using SPR and ELISA comparison methodologies. SPR immunosensory detection provided a precise, sensitive strategy, along with real-time determination, for quantifying adalimumab, having great potential for clinical routine regarding TDM.
Keywords: biological drug; optical biosensor; therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bendtzen K., Svenson M. Detection and Quantification of Antibodies to Biopharmaceuticals. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2011. Enzyme Immunoassays and Radioimmunoassays for Quantification of Anti-TNF Biopharmaceuticals and Anti-Drug Antibodies.
-
- European Medicines Agency Guideline on Immunogenicity Assessment of Biotechnology-Derived Therapeutic Proteins. [(accessed on 3 November 2017)];2015 Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guidelin....
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Biosimilars Guidances. US FDA; New Hampshire, MD, USA: 2017.
-
- WHO (World Health Organization) Guidelines of Evaluation for Similar Biotherapeutics Products (SBPs) [(accessed on 21 February 2018)];2009 Available online: http://www.who.int/biologicals/areas/biological_therapeutics/BIOTHERAPEU....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

