Characterization of Camptothecin-induced Genomic Changes in the Camptothecin-resistant T-ALL-derived Cell Line CPT-K5
- PMID: 29496689
- PMCID: PMC5892604
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20068
Characterization of Camptothecin-induced Genomic Changes in the Camptothecin-resistant T-ALL-derived Cell Line CPT-K5
Abstract
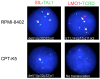
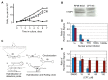
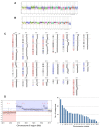
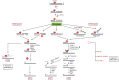
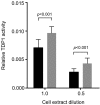
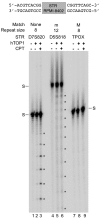
Acquisition of resistance to topoisomerase I (TOP1)-targeting camptothecin (CPT) derivatives is a major clinical problem. Little is known about the underlying chromosomal and genomic mechanisms. We characterized the CPT-K5 cell line expressing mutant CPT-resistant TOP1 and its parental T-cell derived acute lymphoblastic leukemia CPT-sensitive RPMI-8402 cell line by karyotyping and molecular genetic methods, including subtractive oligo-based array comparative genomic hybridization (soaCGH) analysis. Karyotyping revealed that CPT-K5 cells had acquired additional structural aberrations and a reduced modal chromosomal number compared to RPMI-8402. soaCGH analysis identified vast copy number alterations and >200 unbalanced DNA breakpoints distributed unevenly across the chromosomal complement in CPT-K5. In addition, the short tandem repeat alleles were found to be highly different between CPT-K5 and its parental cell line. We identified copy number alterations affecting genes important for maintaining genome integrity and reducing CPT-induced DNA damage. We show for the first time that short tandem repeats are targets for TOP1 cleavage, that can be differentially stimulated by CPT.
Keywords: CPT-K5; aCGH; camptothecin resistance; genomic instability; karyotype; short tandem repeat.
Copyright© 2018, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of a novel topoisomerase I mutation from a camptothecin-resistant human prostate cancer cell line.Cancer Res. 2001 Mar 1;61(5):1964-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11280753
-
Molecular cloning of a cDNA of a camptothecin-resistant human DNA topoisomerase I and identification of mutation sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):69-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.69. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991. PMID: 1849260 Free PMC article.
-
Retroviral expression of a mutant (Gly-533) human DNA topoisomerase I cDNA confers a dominant form of camptothecin resistance.Int J Cancer. 1999 Mar 31;81(1):134-40. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990331)81:1<134::aid-ijc22>3.0.co;2-y. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10077164
-
Topoisomerase degradation, DSB repair, p53 and IAPs in cancer cell resistance to camptothecin-like topoisomerase I inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1835(1):11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23006513 Review.
-
7-Ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxy camptothecin: mechanism of resistance and clinical trials.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1994;34 Suppl:S112-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00684874. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 8070019 Review.
Cited by
-
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, berberine and coptisine, act against camptothecin-resistant topoisomerase I mutants.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):7718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87344-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33833336 Free PMC article.
-
Simple and Fast DNA Based Sensor System for Screening of Small-Molecule Compounds Targeting Eukaryotic Topoisomerase 1.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 13;13(8):1255. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081255. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452216 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of action of non-camptothecin inhibitor Genz-644282 in topoisomerase I inhibition.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 16;5(1):982. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03920-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36114357 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the prognosis in patients with small-cell lung cancer treated by chemotherapy using tumor shrinkage rate-based radiomics.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Aug 2;29(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02001-4. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39095855 Free PMC article.
-
ERH Impacts Patient Prognosis and Tumor Immune Microenvironment: A Pan-Cancer Analysis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(5):853-871. doi: 10.2174/0113862073295696240322084341. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38584561
References
-
- Kantarjian HM, Beran M, Ellis A, Zwelling L, O’Brien S, Cazenave L, Koller C, Rios MB, Plunkett W, Keating MJ. Phase I study of Topotecan, a new topoisomerase I inhibitor, in patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. Blood. 1993;81:1146–1151. - PubMed
-
- Smith DH, Adams JR, Johnston SR, Gordon A, Drummond MF, Bennett CL. A comparative economic analysis of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin versus topotecan in ovarian cancer in the USA and the UK. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:1590–1597. - PubMed
-
- Tsavaris N, Kosmas C, Skopelitis H, Papadoniou N, Polyzos A, Zografos G, Adoniou E, Gryniatsos J, Felekouras E, Zacharakis M, Sigala F, Bacoyiannis C, Papastratis G, Papalambros E. Sequential administration of 5-fluorouracil (5FU)/leucovorin (LV) followed by irinotecan (CPT-11) at relapse versus CPT-11 followed by 5-FU/LV in advanced colorectal carcinoma. A phase III randomized study. Chemotherapy. 2007;53:282–291. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J, Alakl M, Gruia G, Awad L, Rougier P. Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355:1041–1047. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
