LINE-1 ORF1 Protein Is Up-regulated by Reactive Oxygen Species and Associated with Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Progression
- PMID: 29496693
- PMCID: PMC5892605
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20072
LINE-1 ORF1 Protein Is Up-regulated by Reactive Oxygen Species and Associated with Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Progression
Abstract
Background/aim: Reactivation of long interspersed nuclear element-1 (LINE-1) and oxidative stress are suggested to have oncogenic potential to drive tumorigenesis and cancer progression. We previously demonstrated that reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused hypomethylation of LINE-1 elements in bladder cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the expression of LINE-1-encoded protein (ORF1p) and oxidative stress marker 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in human bladder cancer tissues, as well as induction of ORF1p expression by ROS in bladder cancer cell lines.
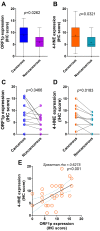
Materials and methods: Thirty-six cancerous and 15 non-cancerous adjacent tissues were immunohistochemically stained for ORF1p and 4-HNE. ORF1p expression and cell migration were determined in bladder cancer cells exposed to H2O2 Results: ORF1p and 4-HNE expression was higher in cancerous than non-cancerous tissues. Elevated ORF1p expression was associated with increased 4-HNE expression and with advanced tumors. H2O2 provoked oxidative stress and up-regulated ORF1p expression in VM-CUB-1 compared to the untreated control, and to a lesser degree in TCCSUP. H2O2 exposure enhanced cell migration in UM-UC-3, TCCSUP and VM-CUB-1.
Conclusion: Elevated ORF1p expression is associated with tumor progression. ROS experimentally induce ORF1p expression and promote migration in bladder cancer cells.
Keywords: 4-HNE; LINE-1; ORF1p; bladder cancer; cancer progression; immunohistochemistry; oxidative stress.
Copyright© 2018, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress and LINE-1 reactivation in bladder cancer are epigenetically linked through active chromatin formation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Apr;134:419-428. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30703483
-
Oxidative stress induces hypomethylation of LINE-1 and hypermethylation of the RUNX3 promoter in a bladder cancer cell line.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(6):3773-8. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.6.3773. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23886181
-
LINE-1 hypomethylation induced by reactive oxygen species is mediated via depletion of S-adenosylmethionine.Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Aug;33(6):375-85. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3124. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Cell Biochem Funct. 2015. PMID: 26178977
-
Current updates on the role of reactive oxygen species in bladder cancer pathogenesis and therapeutics.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Oct;22(10):1687-1697. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02330-w. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32189139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species-mediated therapeutic control of bladder cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2011 Oct 4;8(11):608-16. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2011.135. Nat Rev Urol. 2011. PMID: 21971316 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 23;23(15):8122. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological differences underlying sex and gender disparities in bladder cancer: current synopsis and future directions.Oncogenesis. 2023 Sep 4;12(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41389-023-00489-9. Oncogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37666817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress Markers in Urine and Serum of Patients with Bladder Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;12(2):277. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020277. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829836 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Aging: The proxy of Time.Int Neurourol J. 2022 Mar;26(1):1-2. doi: 10.5213/inj.2222edi01. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Int Neurourol J. 2022. PMID: 35368180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Research progress of LINE-1 in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of gynecologic tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 20;13:1201568. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1201568. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, Lehoczky J, LeVine R, McEwan P, McKernan K, Meldrim J, Mesirov JP, Miranda C, Morris W, Naylor J, Raymond C, Rosetti M, Santos R, Sheridan A, Sougnez C, Stange-Thomann Y, Stojanovic N, Subramanian A, Wyman D, Rogers J, Sulston J, Ainscough R, Beck S, Bentley D, Burton J, Clee C, Carter N, Coulson A, Deadman R, Deloukas P, Dunham A, Dunham I, Durbin R, French L, Grafham D, Gregory S, Hubbard T, Humphray S, Hunt A, Jones M, Lloyd C, McMurray A, Matthews L, Mercer S, Milne S, Mullikin JC, Mungall A, Plumb R, Ross M, Shownkeen R, Sims S, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Hillier LW, McPherson JD, Marra MA, Mardis ER, Fulton LA, Chinwalla AT, Pepin KH, Gish WR, Chissoe SL, Wendl MC, Delehaunty KD, Miner TL, Delehaunty A, Kramer JB, Cook LL, Fulton RS, Johnson DL, Minx PJ, Clifton SW, Hawkins T, Branscomb E, Predki P, Richardson P, Wenning S, Slezak T, Doggett N, Cheng JF, Olsen A, Lucas S, Elkin C, Uberbacher E, Frazier M, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Scherer SE, Bouck JB, Sodergren EJ, Worley KC, Rives CM, Gorrell JH, Metzker ML, Naylor SL, Kucherlapati RS, Nelson DL, Weinstock GM, Sakaki Y, Fujiyama A, Hattori M, Yada T, Toyoda A, Itoh T, Kawagoe C, Watanabe H, Totoki Y, Taylor T, Weissenbach J, Heilig R, Saurin W, Artiguenave F, Brottier P, Bruls T, Pelletier E, Robert C, Wincker P, Smith DR, Doucette-Stamm L, Rubenfield M, Weinstock K, Lee HM, Dubois J, Rosenthal A, Platzer M, Nyakatura G, Taudien S, Rump A, Yang H, Yu J, Wang J, Huang G, Gu J, Hood L, Rowen L, Madan A, Qin S, Davis RW, Federspiel NA, Abola AP, Proctor MJ, Myers RM, Schmutz J, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Cox DR, Olson MV, Kaul R, Raymond C, Shimizu N, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Evans GA, Athanasiou M, Schultz R, Roe BA, Chen F, Pan H, Ramser J, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, McCombie WR, de la Bastide M, Dedhia N, Blocker H, Hornischer K, Nordsiek G, Agarwala R, Aravind L, Bailey JA, Bateman A, Batzoglou S, Birney E, Bork P, Brown DG, Burge CB, Cerutti L, Chen HC, Church D, Clamp M, Copley RR, Doerks T, Eddy SR, Eichler EE, Furey TS, Galagan J, Gilbert JG, Harmon C, Hayashizaki Y, Haussler D, Hermjakob H, Hokamp K, Jang W, Johnson LS, Jones TA, Kasif S, Kaspryzk A, Kennedy S, Kent WJ, Kitts P, Koonin EV, Korf I, Kulp D, Lancet D, Lowe TM, McLysaght A, Mikkelsen T, Moran JV, Mulder N, Pollara VJ, Ponting CP, Schuler G, Schultz J, Slater G, Smit AF, Stupka E, Szustakowki J, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Wagner L, Wallis J, Wheeler R, Williams A, Wolf YI, Wolfe KH, Yang SP, Yeh RF, Collins F, Guyer MS, Peterson J, Felsenfeld A, Wetterstrand KA, Patrinos A, Morgan MJ, de Jong P, Catanese JJ, Osoegawa K, Shizuya H, Choi S, Chen YJ, Szustakowki J, International Human Genome Sequencing C Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
