Variant Linkage Analysis Using de Novo Transcriptome Sequencing Identifies a Conserved Phosphine Resistance Gene in Insects
- PMID: 29496747
- PMCID: PMC5937174
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.118.300688
Variant Linkage Analysis Using de Novo Transcriptome Sequencing Identifies a Conserved Phosphine Resistance Gene in Insects
Abstract
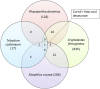
Next-generation sequencing methods enable identification of the genetic basis of traits in species that have no prior genomic information available. The combination of next-generation sequencing, variant analysis, and linkage is a powerful way of identifying candidate genes for a trait of interest. Here, we used a comparative transcriptomics [RNA sequencing (RNAseq)] and genetic linkage analysis approach to identify the rph1 gene. rph1 variants are responsible for resistance to the fumigant phosphine (PH3) that is used to control insect pests of stored grain. In each of the four major species of pest insect of grain we have investigated, there are two major resistance genes, rph1 and rph2, which interact synergistically to produce strongly phosphine-resistant insects. Using RNAseq and genetic linkage analyses, we identified candidate resistance (rph1) genes in phosphine-resistant strains of three species: Rhyzopertha dominica (129 candidates), Sitophilus oryzae (206 candidates), and Cryptolestes ferrugineus (645 candidates). We then compared these candidate genes to 17 candidate resistance genes previously mapped in Tribolium castaneum and found only one orthologous gene, a cytochrome b5 fatty acid desaturase (Cyt-b5-r), to be associated with the rph1 locus in all four species. This gene had either missense amino acid substitutions and/or insertion/deletions/frameshift variants in each of 18 phosphine-resistant strains that were not observed in the susceptible strains of the four species. We propose a model of phosphine action and resistance in which phosphine induces lipid peroxidation through reactive oxygen species generated by dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, whereas disruption of Cyt-b5-r in resistant insects decreases the polyunsaturated fatty acid content of membranes, thereby limiting the potential for lipid peroxidation.
Keywords: insecticide resistance; linkage; pesticide; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Bolter C. J., Chefurka W., 1990. Extramitochondrial release of hydrogen peroxide from insect and mouse liver mitochondria using the respiratory inhibitors phosphine, myxothiazol, and antimycin and spectral analysis of inhibited cytochromes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 278: 65–72. 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90232-N - DOI - PubMed
-
- Champ B. R., Dyte C. E., 1977. FAO global survey of pesticide susceptibility of stored grain pests. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 25: 49–67.
-
- Chaudhry M. Q., Price N. R., 1992. Comparison of the oxidant damage induced by phosphine and the uptake and tracheal exchange of P-32 radiolabeled phosphine in the susceptible and resistant strains of Rhyzopertha-Dominica (F) (Coleoptera, Bostrychidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 42: 167–179. 10.1016/0048-3575(92)90063-6 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

