Iron Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Amine- and Phosphine-Boranes
- PMID: 29497210
- PMCID: PMC5820755
- DOI: 10.1002/ijch.201700018
Iron Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Amine- and Phosphine-Boranes
Abstract
Catalytic dehydrocoupling methodologies, whereby dihydrogen is released from a substrate (or intermolecularly from two substrates) is a mild and efficient method to construct main group element-main group element bonds, the products of which can be used in advanced materials, and also for the development of hydrogen storage materials. With growing interest in the potential of compounds such as ammonia-borane to act as hydrogen storage materials which contain a high weight% of H2, along with the current heightened interest in base metal catalyzed processes, this review covers recent developments in amine and phosphine dehydrocoupling catalyzed by iron complexes. The complexes employed, products formed and mechanistic proposals will be discussed.
Keywords: dehydropolymerization; heterogeneous catalysis; homogeneous catalysis; iron; main group elements.
Figures

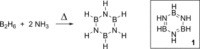
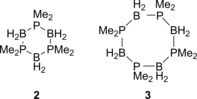
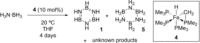
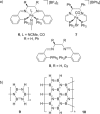


















References
-
- For reviews covering all aspects of main group dehydrocoupling refer to:
-
- Zybill C. E. and Liu C. Y., Synlett 1995, 687–699;
-
- Gauvin F., Harrod J. F., Woo H. G. in Catalytic dehydrocoupling: A general strategy for the formation of element-element bonds, Vol. 42 Eds.: F. G. A. Stone and R. West, Academic Press Limited, London, 1998, pp. 363–405;
-
- Harrod J. F., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 206, 493–531;
-
- Kawakami Y., Li Y., Designed Monomers and Polymers 2000, 3, 399–419;
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
