The neuroprotective role of melatonin in neurological disorders
- PMID: 29498103
- PMCID: PMC6001545
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.24220
The neuroprotective role of melatonin in neurological disorders
Abstract
Melatonin is a neurohormone secreted from the pineal gland and has a wide-ranging regulatory and neuroprotective role. It has been reported that melatonin level is disturbed in some neurological conditions such as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease, which indicates its involvement in the pathophysiology of these diseases. Its properties qualify it to be a promising potential therapeutic neuroprotective agent, with no side effects, for some neurological disorders. This review discusses and localizes the effect of melatonin in the pathophysiology of some diseases.
Keywords: alzheimer; ischemia; melatonin; parkinson.
© 2018 The Authors Journal of Neuroscience Research Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
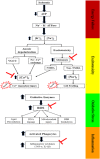
 ) Represents the site of melatonin action
) Represents the site of melatonin action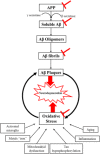
 )
)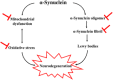
 )
)References
-
- Acuna‐Castroviejo, D. , Coto‐Montes, A. , Gaia Monti, M. , Ortiz, G. G. , & Reiter, R. J. (1997). Melatonin is protective against MPTP‐induced striatal and hippocampal lesions. Life Sciences, 60(2),Pl23–29. - PubMed
-
- Adi, N. , Mash, D. C. , Ali, Y. , Singer, C. , Shehadeh, L. , & Papapetropoulos, S. (2010). Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor expression in Parkinson's disease. Medical Science Monitor, 16(2), Br61–67. - PubMed
-
- Ali, T. , & Kim, M. O. (2015). Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta‐induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3beta pathway in the mouse hippocampus. Journal of Pineal Research, 59(1), 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12238 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alluri, H. , Wilson, R. L. , Anasooya Shaji, C. , Wiggins‐Dohlvik, K. , Patel, S. , Liu, Y. , … Tharakan, B. (2016). Melatonin Preserves Blood‐Brain Barrier Integrity and Permeability via Matrix Metalloproteinase‐9 Inhibition. PLoS One, 11(5), e0154427 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154427 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, A. , Alarcon, R. , Opazo, C. , Campos, E. O. , Munoz, F. J. , Calderon, F. H. , … Inestrosa, N. C. (1998). Stable complexes involving acetylcholinesterase and amyloid‐beta peptide change the biochemical properties of the enzyme and increase the neurotoxicity of Alzheimer's fibrils. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(9), 3213–3223. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

