Characterizing the metabolic phenotype of intestinal villus blunting in Zambian children with severe acute malnutrition and persistent diarrhea
- PMID: 29499047
- PMCID: PMC5834158
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192092
Characterizing the metabolic phenotype of intestinal villus blunting in Zambian children with severe acute malnutrition and persistent diarrhea
Erratum in
-
Correction: Characterizing the metabolic phenotype of intestinal villus blunting in Zambian children with severe acute malnutrition and persistent diarrhea.PLoS One. 2018 May 1;13(5):e0196934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196934. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29715324 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Environmental enteric dysfunction (EED) is widespread throughout the tropics and in children is associated with stunting and other adverse health outcomes. One of the hallmarks of EED is villus damage. In children with severe acute malnutrition (SAM) the severity of enteropathy is greater and short term mortality is high, but the metabolic consequences of enteropathy are unknown. Here, we characterize the urinary metabolic alterations associated with villus health, classic enteropathy biomarkers and anthropometric measurements in severely malnourished children in Zambia.
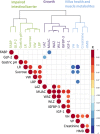
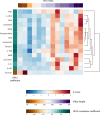
Methods/principal findings: We analysed 20 hospitalised children with acute malnutrition aged 6 to 23 months in Zambia. Small intestinal biopsies were assessed histologically (n = 15), anthropometric and gut function measurements were collected and the metabolic phenotypes were characterized by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Endoscopy could not be performed on community controls children. Growth parameters were inversely correlated with enteropathy biomarkers (p = 0.011) and parameters of villus health were inversely correlated with translocation and permeability biomarkers (p = 0.000 and p = 0.015). Shorter villus height was associated with reduced abundance of metabolites related to gut microbial metabolism, energy and muscle metabolism (p = 0.034). Villus blunting was also related to increased sucrose excretion (p = 0.013).
Conclusions/significance: Intestinal villus blunting is associated with several metabolic perturbations in hospitalized children with severe undernutrition. Such alterations include altered muscle metabolism, reinforcing the link between EED and growth faltering, and a disruption in the biochemical exchange between the gut microbiota and host. These findings extend our understanding on the downstream consequences of villus blunting and provide novel non-invasive biomarkers of enteropathy dysfunction. The major limitations of this study are the lack of comparative control group and gut microbiota characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013;382:427–51. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60937-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Central Statistical Office (CSO), Ministry of Health (MOH), Tropical Diseases Research Centre (TDRC), University of Zambia, and Macro International Inc. Zambia Demographic and Health Survey 2014. Calverton, Maryland, USA: CSO and Macro International Inc; 2015.
-
- Olofin I, McDonald CM, Ezzati M, Flaxman S, Black RE, Fawzi WW, et al. Associations of suboptimal growth with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in children under five years: a pooled analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64636 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064636 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Victora CG, Adair L, Fall C, Hallal PC, Martorell R, Richter L, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: consequences for adult health and human capital. Lancet. 2008;371:340–57. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61692-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

