Building a CAR Garage: Preparing for the Delivery of Commercial CAR T Cell Products at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- PMID: 29499327
- PMCID: PMC6625528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.02.018
Building a CAR Garage: Preparing for the Delivery of Commercial CAR T Cell Products at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Abstract
Two commercial chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies for CD19-expressing B cell malignancies, Kymriah and Yescarta, have recently been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. The administration of CAR T cells is a complex endeavor involving cell manufacture, tracking and shipping of apheresis products, and management of novel and severe toxicities. At Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, we have identified 8 essential tasks that define the CAR T cell workflow. In this review, we discuss practical aspects of CAR T cell program development, including clinical, administrative, and regulatory challenges for successful implementation.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CAR T cells; Cellular therapy; Chimeric antigen receptor; Cytokine release syndrome; Diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
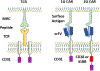

References
-
- Sadelain M Chimeric Antigen Receptors: A Paradigm Shift in Immunotherapy. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 2017;1:447–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-050216-034351. - DOI
-
- Rosenberg SA, John R, Yang JC, et al. Treatment of Patients With Metastatic Melanoma With Autologous Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Interleukin 2. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994;86(15):1159–1166. - PubMed
-
- Eshhar Z, Waks T, Gross G, Schindler DG. Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(2):720–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.720. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

