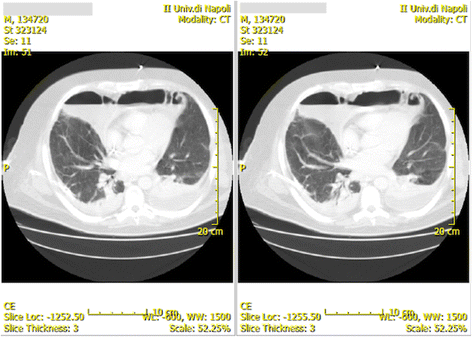
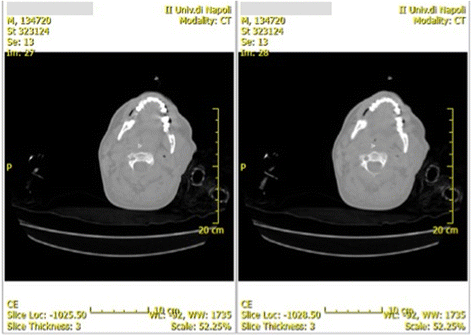
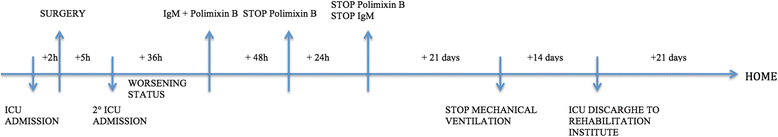
Septic shock from descending necrotizing mediastinitis - combined treatment with IgM-enriched immunoglobulin preparation and direct polymyxin B hemoperfusion: a case report
- PMID: 29499757
- PMCID: PMC5834850
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-018-1611-5
Septic shock from descending necrotizing mediastinitis - combined treatment with IgM-enriched immunoglobulin preparation and direct polymyxin B hemoperfusion: a case report
Abstract
Background: Descending necrotizing mediastinitis is a common and progressive polymicrobial infection involving the neck and chest with a high death rate (10 to 40%). From a microbiological point of view, descending necrotizing mediastinitis is sustained by Gram-positive bacteria (43-62%), anaerobes (46-78%), and, rarely, Gram-negative bacteria. Data collected during the Antibiotic Resistance-Istituto Superiore di Sanità project confirmed that Italy is positioned among the countries with the highest levels of resistance in most pathogenic species under surveillance. In particular, 32.9% of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates were resistant to carbapenem, 33.6% of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin, and 28.7% and 43.9% of Escherichia coli isolates to third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones, respectively.
Case presentation: We describe the case of a 38-year-old white man with septic shock due to descending necrotizing mediastinitis sustained by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria treated after surgery with an IgM-enriched immunoglobulin preparation and polymyxin B hemoperfusion therapy.
Conclusion: Despite the contrasting data on the use of immunoglobulins and polymyxin B hemoperfusion in septic shock and the lack of literature in cases of acute mediastinitis caused by both Gram-negative and Gram-positive multidrug-resistant bacteria, we obtained an improvement in clinical conditions and the survival of our patient, against all odds.
Keywords: IgM-enriched immunoglobulin preparation; Mediastinitis; Polymyxin B hemoperfusion; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors obtained ethics approval and written informed consent. We obtained Ethical Approval for the data publication from ethical Committee (EC).
The authors obtained consent for publication from the patient.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of polymyxin B haemoperfusion on septic shock caused by Gram-positive bacteria.Anaesth Intensive Care. 2025 Mar;53(2):125-135. doi: 10.1177/0310057X241284300. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2025. PMID: 39866022
-
Direct hemoperfusion with a polymyxin B column versus vasopressin for gram negative septic shock: a matched cohort study of the effect on survival.Clin Nephrol. 2013 Jun;79(6):463-70. doi: 10.5414/CN107584. Clin Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23253903
-
Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2009 Jun 17;301(23):2445-52. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.856. JAMA. 2009. PMID: 19531784 Clinical Trial.
-
Endotoxin adsorption: Direct hemoperfusion with the polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column (PMX).Transfus Apher Sci. 2017 Oct;56(5):682-688. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Transfus Apher Sci. 2017. PMID: 28923774 Review.
-
Cervical necrotizing fasciitis with descending mediastinitis: literature review and case report.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012 Jun;70(6):1342-50. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.05.007. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012. PMID: 21820786 Review.
Cited by
-
Best-practice IgM- and IgA-enriched immunoglobulin use in patients with sepsis.Ann Intensive Care. 2020 Oct 7;10(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00740-1. Ann Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 33026597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septic shock due to Escherichia coli meningoencephalitis treated with immunoglobulin-M-enriched immunoglobulin preparation as adjuvant therapy: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Mar 29;15(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02731-7. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33775244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources