Measurement and Estimation of Residual Kidney Function in Patients on Dialysis
- PMID: 29499893
- PMCID: PMC5841591
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ackd.2017.09.001
Measurement and Estimation of Residual Kidney Function in Patients on Dialysis
Abstract
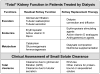
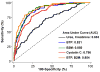
Residual kidney function (RKF) in patients on dialysis is strongly associated with survival and better quality of life. Assessment of kidney function underlies the management of patients with chronic kidney disease before dialysis initiation. However, methods to assess RKF after dialysis initiation are just now being refined. In this review, we discuss the definition of RKF and methods for measurement and estimation of RKF, highlighting the unique aspects of dialysis that impact these assessments.
Keywords: Cystatin C; Glomerular filtration rate; Residual kidney function; β-2 Microglobulin; β-Trace protein.
Copyright © 2017 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Sirich TL, Meyer TW, Gondouin B, Brunet P, Niwa T. Protein-bound molecules: a large family with a bad character. Semin Nephrol. 2014 Mar;34(2):106–117. - PubMed
-
- Lowenstein J, Grantham JJ. Residual renal function: a paradigm shift. Kidney Int. 2017 Mar;91(3):561–565. - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System. 2016 USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD: 2016. [Accessed June 29, 2017].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

