Simvastatin reduces circulating oxysterol levels in men with hypercholesterolaemia
- PMID: 29501047
- PMCID: PMC5952874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.014
Simvastatin reduces circulating oxysterol levels in men with hypercholesterolaemia
Abstract
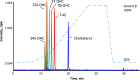
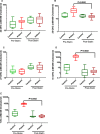
Oxysterols (OHC) are biologically active cholesterol metabolites circulating in plasma that may be formed enzymatically (e.g. 24S-OHC, 25-OHC and 27-OHC) or by autoxidative mechanisms (e.g. 7-ketocholesterol, 7β-OHC and 25-OHC). Oxysterols are more soluble than cholesterol and are reported to exert inflammatory, cytoprotective and apoptotic effects according to concentration and species. Esterified oxysterols have been analysed in people with dementia and cardiovascular diseases although there is no consistent relationship between oxysterol esters and disease. However, oxysterol esters are held in lipoprotein core and may not relate to the concentration and activity of plasma free oxysterols. Methodological limitations have challenged the analysis of free oxysterols to date. We have developed a fast, sensitive and specific quantitative LC-MS/MS, multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) method to target five oxysterols in human plasma with analyte recoveries between 72% and 82% and sensitivities between 5 and 135 pg/ml. A novel method was used to investigate the hypothesis that simvastatin may reduce the concentrations of specific plasma free oxysterols in hypercholesterolaemia. Twenty healthy male volunteers were recruited (aged 41-63 years); ten were asymptomatic with high plasma cholesterol > 6.5 mM and ten were healthy with normal plasma cholesterol (< 6.5 mM). Simvastatin (40 mg/day) was prescribed to those with hypercholesterolaemia. Plasma samples were taken from both groups at baseline and after three months. Simvastatin reduced plasma cholesterol by ~35% (p < 0.05) at the end of three months. Oxysterols generated by autoxidation (but not enzymatically) were elevated up to 45 fold in hypercholesterolaemic midlife men. Plasma oxysterols were restored to those of healthy controls after simvastatin intervention suggesting that autoxidation is either prevented by simvastatin directly or that autoxidation is less prevalent when plasma cholesterol concentrations are within the normal range.
Keywords: Dementia; Hydroxycholesterol; Mass spectrometry; Statin; Vascular disease.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fast LC-MS/MS analysis of free oxysterols derived from reactive oxygen species in human plasma and carotid plaque.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Oct 21;425:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23827692
-
Interactions of Oxysterols with Atherosclerosis Biomarkers in Subjects with Moderate Hypercholesterolemia and Effects of a Nutraceutical Combination (Bifidobacterium longum BB536, Red Yeast Rice Extract) (Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study).Nutrients. 2021 Jan 28;13(2):427. doi: 10.3390/nu13020427. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33525601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reduction of plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol (cerebrosterol) levels using high-dosage simvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: evidence that simvastatin affects cholesterol metabolism in the human brain.Arch Neurol. 2002 Feb;59(2):213-6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.59.2.213. Arch Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11843691 Clinical Trial.
-
New methods for analysis of oxysterols and related compounds by LC-MS.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Sep;162:4-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Nov 27. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26639636 Review.
-
Different functions of vitamin E homologues in the various types of cell death induced by oxysterols.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Nov 20;176:356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34648906 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxysterols and Oxysterol Sulfates in Alzheimer's Disease Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;87(4):1527-1536. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220083. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 35491790 Free PMC article.
-
Memantine, Simvastatin, and Epicatechin Inhibit 7-Ketocholesterol-induced Apoptosis in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells But Not Neurosensory Retinal Cells In Vitro.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020 Oct 25;15(4):470-480. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v15i4.7781. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020. PMID: 33133437 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxes: Cholesterol and Hypoxia in Preeclampsia.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 13;14(6):691. doi: 10.3390/biom14060691. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxysterols: From redox bench to industry.Redox Biol. 2022 Feb;49:102220. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102220. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 34968886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Determination of a Series of Oxysterols by an Optimized LC-MS/MS Analysis in Different Tissue Types.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 25;26(1):77. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010077. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perna L., Mons U., Rujescu D., Kliegel M., Brenner H. Apolipoprotein E e4 and cognitive function: a modifiable association results from two independent cohort studies. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2016;41(1–2):35–45. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A., Jacobs D.R., Jr., Menotti A., Nissinen A., Dontas A., Kafatos A. Cardiovascular risk factors and dementia mortality: 40 years of follow-up in the Seven Countries Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009;280(1–2):79–83. - PubMed
-
- Kivipelto M., Ngandu T., Laatikainen T., Winblad B., Soininen H., Tuomilehto J. Risk score for the prediction of dementia risk in 20 years among middle aged people: a longitudinal, population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(9):735–741. - PubMed
-
- Polidori M.C., Pientka L., Mecocci P. A review of the major vascular risk factors related to Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimer's. Dis.: JAD. 2012;32(3):521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

