Heparin/heparan sulfate analysis by covalently modified reverse polarity capillary zone electrophoresis-mass spectrometry
- PMID: 29501428
- PMCID: PMC5862776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.052
Heparin/heparan sulfate analysis by covalently modified reverse polarity capillary zone electrophoresis-mass spectrometry
Abstract
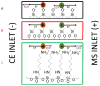
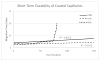
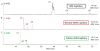
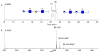
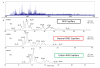
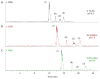
Reverse polarity capillary zone electrophoresis coupled to negative ion mode mass spectrometry (CZE-MS) is shown to be an effective and sensitive tool for the analysis of glycosaminoglycan mixtures. Covalent modification of the inner wall of the separation capillary with neutral or cationic reagents produces a stable and durable surface that provides reproducible separations. By combining CZE-MS with a cation-coated capillary and a sheath flow interface, a rapid and reliable method has been developed for the analysis of sulfated oligosaccharides from dp4 to dp12. Several different mixtures have been separated and detected by mass spectrometry. The mixtures were selected to test the capability of this approach to resolve subtle differences in structure, such as sulfation position and epimeric variation of the uronic acid. The system was applied to a complex mixture of heparin/heparan sulfate oligosaccharides varying in chain length from dp3 to dp12 and more than 80 molecular compositions were identified by accurate mass measurement.
Keywords: Capillary zone electrophoresis; Covalent capillary coating; Mass spectrometry; Mixture analysis; Reverse polarity; Sulfated glycosaminoglycan.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Varki A, Cummings R, Esko J, Freeze H, Hart G, Marth J. Essentials of glycobiology. 1998 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

