Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers measured by Elecsys assays compared to amyloid imaging
- PMID: 29501462
- PMCID: PMC6119652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.01.013
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers measured by Elecsys assays compared to amyloid imaging
Abstract
Introduction: Levels of amyloid β peptide 42 (Aβ42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau-181 are well-established cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease, but variability in manual plate-based assays has limited their use. We examined the relationship between CSF biomarkers, as measured by a novel automated immunoassay platform, and amyloid positron emission tomography.
Methods: CSF samples from 200 individuals underwent separate analysis for Aβ42, total tau, and phosphorylated tau-181 with automated Roche Elecsys assays. Aβ40 was measured with a commercial plate-based assay. Positron emission tomography with Pittsburgh Compound B was performed less than 1 year from CSF collection.
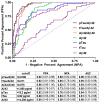
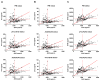
Results: Ratios of CSF biomarkers (total tau/Aβ42, phosphorylated tau-181/Aβ42, and Aβ42/Aβ40) best discriminated Pittsburgh Compound B-positive from Pittsburgh Compound B-negative individuals.
Discussion: CSF biomarkers and amyloid positron emission tomography reflect different aspects of Alzheimer's disease brain pathology, and therefore, less-than-perfect correspondence is expected. Automated assays are likely to increase the utility of CSF biomarkers.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid; Biomarker; Cerebrospinal fluid; Cutoff.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
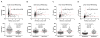
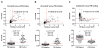
References
-
- Price JL, Morris JC. Tangles and plaques in nondemented aging and “preclinical” Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of neurology. 1999;45:358–68. - PubMed
-
- Fagan AM, Mintun MA, Mach RH, Lee SY, Dence CS, Shah AR, et al. Inverse relation between in vivo amyloid imaging load and cerebrospinal fluid Abeta42 in humans. Annals of neurology. 2006;59:512–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034119/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG053474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG053550/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG053426/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB009352/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS098577/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG050921/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

