Partial exposure of frog heart to high-potassium solution: an easily reproducible model mimicking ST segment changes
- PMID: 29503350
- PMCID: PMC5938182
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.18-0010
Partial exposure of frog heart to high-potassium solution: an easily reproducible model mimicking ST segment changes
Abstract
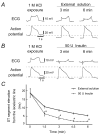
By simply inducing burn injuries on the bullfrog heart, we previously reported a simple model of abnormal ST segment changes observed in human ischemic heart disease. In the present study, instead of inducing burn injuries, we partially exposed the surface of the frog heart to high-potassium (K+) solution to create a concentration gradient of the extracellular K+ within the myocardium. Dual recordings of ECG and the cardiac action potential demonstrated significant elevation of the ST segment and the resting membrane potential, indicating its usefulness as a simple model of heart injury. Additionally, from our results, Na+/K+-ATPase activity was thought to be primarily responsible for generating the K+ concentration gradient and inducing the ST segment changes in ECG.
Keywords: Na+/K+-ATPase activity; ST segment change; bullfrog heart; ischemic heart disease; partial exposure to high-potassium solution.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Subepicardial burn injuries in bullfrog heart induce electrocardiogram changes mimicking inferior wall myocardial infarction.J Vet Med Sci. 2022 Sep 1;84(9):1205-1210. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0243. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35811132 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal ST segment changes reproduced in burn-induced subepicardial injury model in bullfrog heart.J Vet Med Sci. 2020 Feb 4;82(2):143-147. doi: 10.1292/jvms.19-0597. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Vet Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31827015 Free PMC article.
-
High-magnesium exposure to bullfrog heart causes ST segment elevation.J Vet Med Sci. 2021 Apr 9;83(4):675-679. doi: 10.1292/jvms.20-0720. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Vet Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33612659 Free PMC article.
-
Potassium metabolism in the normal and ischemic heart cell.Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1976 Jun;13(4):269-91. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1976. PMID: 786907 Review.
-
Clinical correlates of the electrophysiologic action of digitalis on the heart.Semin Drug Treat. 1972 Autumn;2(2):179-201. Semin Drug Treat. 1972. PMID: 4343767 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Subepicardial burn injuries in bullfrog heart induce electrocardiogram changes mimicking inferior wall myocardial infarction.J Vet Med Sci. 2022 Sep 1;84(9):1205-1210. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0243. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35811132 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent ST elevation in right bundle branch block pseudo-mimicking myocardial infarction.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019 Feb 4;7:2050313X19827748. doi: 10.1177/2050313X19827748. eCollection 2019. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30783529 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal ST segment changes reproduced in burn-induced subepicardial injury model in bullfrog heart.J Vet Med Sci. 2020 Feb 4;82(2):143-147. doi: 10.1292/jvms.19-0597. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Vet Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31827015 Free PMC article.
-
Amitriptyline intoxication in bullfrogs causes widening of QRS complexes in electrocardiogram.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Feb 1;85(2):175-179. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0494. Epub 2022 Dec 29. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36596558 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin accelerates recovery from QRS complex widening in a frog heart model of hyperkalemia.J Vet Med Sci. 2021 Dec 2;83(12):1855-1859. doi: 10.1292/jvms.21-0481. Epub 2021 Oct 18. J Vet Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34657900 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

