Comparison of two laboratory-based systems for evaluation of halos in intraocular lenses
- PMID: 29503526
- PMCID: PMC5826305
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S152201
Comparison of two laboratory-based systems for evaluation of halos in intraocular lenses
Abstract
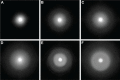
Purpose: Multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) can be associated with unwanted visual phenomena, including halos. Predicting potential for halos is desirable when designing new multifocal IOLs. Halo images from 6 IOL models were compared using the Optikos modulation transfer function bench system and a new high dynamic range (HDR) system.
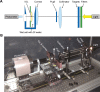
Materials and methods: One monofocal, 1 extended depth of focus, and 4 multifocal IOLs were evaluated. An off-the-shelf optical bench was used to simulate a distant (>50 m) car headlight and record images. A custom HDR system was constructed using an imaging photometer to simulate headlight images and to measure quantitative halo luminance data. A metric was developed to characterize halo luminance properties. Clinical relevance was investigated by correlating halo measurements to visual outcomes questionnaire data.
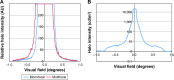
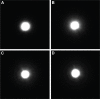
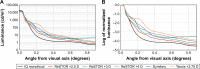
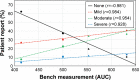
Results: The Optikos system produced halo images useful for visual comparisons; however, measurements were relative and not quantitative. The HDR halo system provided objective and quantitative measurements used to create a metric from the area under the curve (AUC) of the logarithmic normalized halo profile. This proposed metric differentiated between IOL models, and linear regression analysis found strong correlations between AUC and subjective clinical ratings of halos.
Conclusion: The HDR system produced quantitative, preclinical metrics that correlated to patients' subjective perception of halos.
Keywords: high dynamic range; multifocal IOL; quantitative metric; visual disturbance.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Daniel Carson, Sangyeol Lee, Xin Wei, and Shinwook Lee are employees of Alcon. Elsinore Alexander was an employee of Alcon at the time of the study. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Lundstrom M, Barry P, Henry Y, Rosen P, Stenevi U. Evidence-based guidelines for cataract surgery: guidelines based on data in the European Registry of Quality Outcomes for Cataract and Refractive Surgery database. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38(6):1086–1093. - PubMed
-
- Olson RJ, Braga-Mele R, Chen SH, et al. Cataract in the adult eye preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology. 2017;124(2):P1–P119. - PubMed
-
- Jaycock P, Johnston RL, Taylor H, et al. UK EPR User Group The Cataract National Dataset electronic multi-centre audit of 55,567 operations: updating benchmark standards of care in the United Kingdom and internationally. Eye (Lond) 2009;23(1):38–49. - PubMed
-
- Calladine D, Evans JR, Shah S, Leyland M. Multifocal versus monofocal intraocular lenses after cataract extraction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(9):CD003169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

