Characterization of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor type I (LH-RH-I) as a potential molecular target in OCM-1 and OCM-3 human uveal melanoma cell lines
- PMID: 29503568
- PMCID: PMC5826244
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S148174
Characterization of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor type I (LH-RH-I) as a potential molecular target in OCM-1 and OCM-3 human uveal melanoma cell lines
Abstract
Introduction: Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most common primary intraocular malignancy with very poor prognosis. Conventional chemotherapy only rarely prolongs the survival, therefore patients require novel treatment modalities. The discovery of specific receptors for hypothalamic hormones on cancer cells has led to the development of radiolabeled and cytotoxic hormone analogs.
Materials and methods: In the present study, our aim was to investigate the expression of mRNA for receptors of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone type I (LH-RH-I) and LH-RH ligand in OCM-1 and OCM-3 human uveal melanoma cell lines. The presence and binding characteristics of LH-RH-I receptor protein was further studied by Western blot, immunocytochemistry and ligand competition assay. The expression of mRNA and protein for LH-RH-I receptors has been also studied using tumor samples originating from nude mice xenografted with OCM-1 or OCM-3 cells.
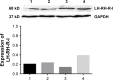
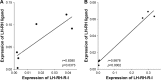
Results: The mRNA for LH-RH-I receptor has been detected in OCM-1 and OCM-3 cell lines and was found markedly higher in OCM-3 cells. The mRNA for LH-RH-I receptors was also observed in both UM xenograft models in vivo with higher levels in OCM-3. The presence of LH-RH-I receptor protein was found in both cell lines in vitro by immunocytochemistry and Western blot, and also in tumor tissue samples grown in nude mice by Western blot. Both human uveal melanoma models investigated showed specific high affinity receptors for LH-RH-I using ligand competition assay. The mRNA for LH-RH ligand has also been detected in OCM-1 and OCM-3 cell lines and cancer tissues.
Conclusion: The demonstration of the expression of LH-RH-I receptors in OCM-1 and OCM-3 human UM cell lines suggests that they could serve as potential molecular target for therapy. Our findings support the development of new therapeutic approaches based on cytotoxic LH-RH analogs or modern powerful antagonistic analogs of LH-RH targeting LH-RH-I receptors in UM.
Keywords: LH-RH ligand; LH-RH receptor; human uveal melanoma; targeted cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interests in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Petrausch U, Martus P, Tönnies H, et al. Significance of gene expression analysis in uveal melanoma in comparison to standard risk factors for risk assessment of subsequent metastases. Eye (Lond) 2008;22(8):997–1007. - PubMed
-
- Dopierala J, Damato BE, Lake SL, Taktak AFG, Coupland SE. Genetic heterogeneity in uveal melanoma assessed by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(10):4898–4905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

