Risk factors associated with postoperative pain and discomfort in oculoplastic surgery with general anesthesia: a prospective study
- PMID: 29503577
- PMCID: PMC5827462
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S156104
Risk factors associated with postoperative pain and discomfort in oculoplastic surgery with general anesthesia: a prospective study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate patient pain and discomfort following oculoplastic surgery performed under general anesthesia and to assess key factors associated with postoperative pain and discomfort.
Methods: A prospective observational cohort study was conducted among 212 consecutive patients who underwent oculoplastic surgery performed under general anesthesia. The patients were assessed according to quantified levels of pain and discomfort postoperatively. Analgesic requests were recorded, and responses were statistically analyzed.
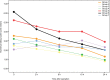
Results: Pain and discomfort after oculoplastic surgery under general anesthesia were reported by 32.1% and 28.3% of the patients, respectively; 2.8% of the patients requested analgesic medication within 18 hours after surgery. The patients who underwent orbital decompression, secondary orbital implantation, and orbital fracture repair were more likely to develop significant postoperative pain and discomfort (P<0.001), and the patients who underwent enucleation/evisceration during orbital implantation were more likely to develop postoperative discomfort (P<0.001). The predictors of pain were smoking history, prior surgery on the operative eye, and anxiety (P<0.05), and the predictor of discomfort was anxiety (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Patients undergoing oculoplastic surgery tend to experience postoperative pain and discomfort. Anxiety is a risk factor for both postoperative pain and discomfort, while smoking history and prior surgery on the operative eye may be associated with postoperative pain.
Keywords: Chinese; discomfort level; ophthalmic surgery; pain level; prevalence; related factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Myles PS, Williams DL, Hendrata M, Anderson H, Weeks AM. Patient satisfaction after anaesthesia and surgery: results of a prospective survey of 10,811 patients. Br J Anaesth. 2000;84(1):6–10. - PubMed
-
- Sommer M, Geurts JW, Stessel B, et al. Prevalence and predictors of postoperative pain after ear, nose, and throat surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;135(2):124–130. - PubMed
-
- Henzler D, Kramer R, Steinhorst UH, Piepenbrock S, Rossaint R, Kuhlen R. Factors independently associated with increased risk of pain development after ophthalmic surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004;21(2):101–106. - PubMed
-
- Lesin M, Domazet Bugarin J, Puljak L. Factors associated with postoperative pain and analgesic consumption in ophthalmic surgery: a systematic review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2015;60(3):196–203. - PubMed
-
- Lesin M, Sundov ZD, Jukic M, Puljak L. Postoperative pain in complex ophthalmic surgical procedures: comparing practice with guidelines. Pain Med. 2014;15(6):1036–1042. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

