Arabidopsis EMB1990 Encoding a Plastid-Targeted YlmG Protein Is Required for Chloroplast Biogenesis and Embryo Development
- PMID: 29503657
- PMCID: PMC5820536
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00181
Arabidopsis EMB1990 Encoding a Plastid-Targeted YlmG Protein Is Required for Chloroplast Biogenesis and Embryo Development
Abstract
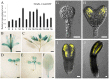
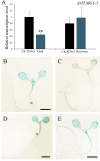
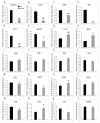
In higher plants, embryo development originated from fertilized egg cell is the first step of the life cycle. The chloroplast participates in many essential metabolic pathways, and its function is highly associated with embryo development. However, the mechanisms and relevant genetic components by which the chloroplast functions in embryogenesis are largely uncharacterized. In this paper, we describe the Arabidopsis EMB1990 gene, encoding a plastid-targeted YlmG protein which is required for chloroplast biogenesis and embryo development. Loss of the EMB1990/YLMG1-1 resulted in albino seeds containing abortive embryos, and the morphological development of homozygous emb1990 embryos was disrupted after the globular stage. Our results showed that EMB1990/YLMG1-1 was expressed in the primordia and adaxial region of cotyledon during embryogenesis, and the encoded protein was targeted to the chloroplast. TEM observation of cellular ultrastructure showed that chloroplast biogenesis was impaired in emb1990 embryo cells. Expression of certain plastid genes was also affected in the loss-of-function mutants, including genes encoding core protein complex subunits located in the thylakoid membrane. Moreover, the tissue-specific genes of embryo development were misexpressed in emb1990 mutant, including genes known to delineate cell fate decisions in the SAM (shoot apical meristem), cotyledon and hypophysis. Taken together, we propose that the nuclear-encoded YLMG1-1 is targeted to the chloroplast and required for normal plastid gene expression. Hence, YLMG1-1 plays a critical role in Arabidopsis embryogenesis through participating in chloroplast biogenesis.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; YLMG; chloroplast; embryo development; plastid gene expression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EMB2738, which encodes a putative plastid-targeted GTP-binding protein, is essential for embryogenesis and chloroplast development in higher plants.Physiol Plant. 2017 Nov;161(3):414-430. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12603. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Physiol Plant. 2017. PMID: 28675462
-
Translocase of the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane 40 Is Required for Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Embryo Development in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Apr 2;10:389. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00389. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31001303 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonuclease J is required for chloroplast and embryo development in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(7):2079-91. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv010. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25871650 Free PMC article.
-
EMB1211 is required for normal embryo development and influences chloroplast biogenesis in Arabidopsis.Physiol Plant. 2010 Dec;140(4):380-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2010.01407.x. Physiol Plant. 2010. PMID: 20738804
-
Chloroplast RNA polymerases: Role in chloroplast biogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1847(9):761-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25680513 Review.
Cited by
-
GWAS and transcriptome analysis reveal MADS26 involved in seed germination ability in maize.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 May;135(5):1717-1730. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04065-4. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 35247071
-
The J-like domain CPP1-homolog CPL3 exclusively localizes in plastids and is not a key regulator of plant photomorphogenesis.Plant Physiol. 2025 Aug 4;198(4):kiaf343. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf343. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40794802 Free PMC article.
-
Cytological, genetic and transcriptomic characterization of a cucumber albino mutant.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 20;13:1047090. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1047090. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340338 Free PMC article.
-
ylm Has More than a (Z Anchor) Ring to It!J Bacteriol. 2021 Jan 11;203(3):e00460-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00460-20. Print 2021 Jan 11. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 32900832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome characteristics during cell wall formation of endosperm cellularization and embryo differentiation in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 3;13:998664. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.998664. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36262665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berleth T., Jürgens G. (1993). The role of the monopteros gene in organizing the basal body region of the Arabidopsis embryo. Development 118 575–587. 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90246-E - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

