Accuracy and reproducibility of 3D digital tooth preparations made by gypsum materials of various colors
- PMID: 29503709
- PMCID: PMC5829291
- DOI: 10.4047/jap.2018.10.1.8
Accuracy and reproducibility of 3D digital tooth preparations made by gypsum materials of various colors
Abstract
Purpose: The study aimed to identify the accuracy and reproducibility of preparations made by gypsum materials of various colors using quantitative and semi-quantitative three-dimensional (3D) approach.
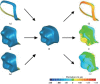
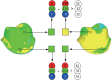
Materials and methods: A titanium maxillary first molar preparation was created as reference dataset (REF). Silicone impressions were duplicated from REF and randomized into 6 groups (n=8). Gypsum preparations were formed and grouped according to the color of gypsum materials, and light-scanned to obtain prepared datasets (PRE). Then, in terms of accuracy, PRE were superimposed on REF using the best-fit-algorithm and PRE underwent intragroup pairwise best-fit alignment for assessing reproducibility. Root mean square deviation (RMSD) and degrees of similarity (DS) were computed and analyzed with SPSS 20.0 statistical software (α=.05).
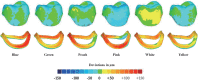
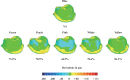
Results: In terms of accuracy, PREs in 3D directions were increased in the 6 color groups (from 19.38 to 20.88 µm), of which the marginal and internal variations ranged 51.36 - 58.26 µm and 18.33 - 20.04 µm, respectively. On the other hand, RMSD value and DS-scores did not show significant differences among groups. Regarding reproducibility, both RMSD and DS-scores showed statistically significant differences among groups, while RMSD values of the 6 color groups were less than 5 µm, of which blue color group was the smallest (3.27 ± 0.24 µm) and white color group was the largest (4.24 ± 0.36 µm). These results were consistent with the DS data.
Conclusion: The 3D volume of the PREs was predisposed towards an increase during digitalization, which was unaffected by gypsum color. Furthermore, the reproducibility of digitalizing scanning differed negligibly among different gypsum colors, especially in comparison to clinically observed discrepancies.
Keywords: Accuracy; Color; Dental gypsum materials; Reproducibility; Three-dimensional analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of CNC-milling on the marginal and internal fit of dental ceramics: a pilot study.Dent Mater. 2013 Aug;29(8):851-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2013.04.018. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Dent Mater. 2013. PMID: 23743092
-
Qualitative and quantitative three-dimensional accuracy of a single tooth captured by elastomeric impression materials: an in vitro study.J Prosthet Dent. 2012 Sep;108(3):165-72. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(12)60141-3. J Prosthet Dent. 2012. PMID: 22944312
-
Three-Dimensional Evaluation on Accuracy of Conventional and Milled Gypsum Models and 3D Printed Photopolymer Models.Materials (Basel). 2019 Oct 25;12(21):3499. doi: 10.3390/ma12213499. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31731447 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of 3D Printed Models Created by Two Technologies of Printers with Different Designs of Model Base.J Prosthodont. 2020 Feb;29(2):124-128. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13107. Epub 2019 Sep 9. J Prosthodont. 2020. PMID: 31498957 Review.
-
Influence of Tooth Preparation Design and Scan Angulations on the Accuracy of Two Intraoral Digital Scanners: An in Vitro Study Based on 3-Dimensional Comparisons.J Prosthodont. 2020 Mar;29(3):201-206. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13148. Epub 2020 Feb 13. J Prosthodont. 2020. PMID: 31994818 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Intaglio Surface Trueness of Interim Dental Crowns Fabricated with SLA 3D Printing, DLP 3D Printing, and Milling Technologies.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Aug 3;9(8):983. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9080983. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keshvad A, Hooshmand T, Asefzadeh F, Khalilinejad F, Alihemmati M, Van Noort R. Marginal gap, internal fit, and fracture load of leucite-reinforced ceramic inlays fabricated by CEREC inLab and hot-pressed techniques. J Prosthodont. 2011;20:535–540. - PubMed
-
- Eisenburger M, Shellis RP, Addy M. Comparative study of wear of enamel induced by alternating and simultaneous combinations of abrasion and erosion in vitro. Caries Res. 2003;37:450–455. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett DW, Blunt L, Smith BG. Measurement of tooth wear in patients with palatal erosion. Br Dent J. 1997;182:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Azzopardi A, Bartlett DW, Watson TF, Sherriff M. The measurement and prevention of erosion and abrasion. J Dent. 2001;29:395–400. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

