Bayesian-Based Decision Support System for Assessing the Needs for Orthodontic Treatment
- PMID: 29503749
- PMCID: PMC5820082
- DOI: 10.4258/hir.2018.24.1.22
Bayesian-Based Decision Support System for Assessing the Needs for Orthodontic Treatment
Abstract
Objectives: In this study, a clinical decision support system was developed to help general practitioners assess the need for orthodontic treatment in patients with permanent dentition.
Methods: We chose a Bayesian network (BN) as the underlying model for assessing the need for orthodontic treatment. One thousand permanent dentition patient data sets chosen from a hospital record system were prepared in which one data element represented one participant with information for all variables and their stated need for orthodontic treatment. To evaluate the system, we compared the assessment results based on the judgements of two orthodontists to those recommended by the decision support system.
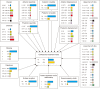
Results: In a BN decision support model, each variable is modelled as a node, and the causal relationship between two variables may be represented as a directed arc. For each node, a conditional probability table is supplied that represents the probabilities of each value of this node, given the conditions of its parents. There was a high degree of agreement between the two orthodontists (kappa value = 0.894) in their diagnoses and their judgements regarding the need for orthodontic treatment. Also, there was a high degree of agreement between the decision support system and orthodontists A (kappa value = 1.00) and B (kappa value = 0.894).
Conclusions: The study was the first testing phase in which the results generated by the proposed system were compared with those suggested by expert orthodontists. The system delivered promising results; it showed a high degree of accuracy in classifying patients into groups needing and not needing orthodontic treatment.
Keywords: Angle's Classification; Artificial Intelligence; Dental Informatics; Machine Learning; Malocclusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Digital images as an alternative to orthodontic casts in assessing malocclusion and orthodontic treatment need.Acta Odontol Scand. 2007 Nov;65(6):362-8. doi: 10.1080/00016350701771850. Acta Odontol Scand. 2007. PMID: 18071959
-
[Orthodontic treatment needs and indications assessed with IONT].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2004;50(1):115-22. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2004. PMID: 16871750 Polish.
-
Assessment of Severity of Malocclusion and Orthodontic Treatment Need Using the Dental Esthetic Index and Angle's Classification: A Retrospective Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021 Oct 1;22(10):1167-1170. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021. PMID: 35197385
-
Perception of orthodontic treatment need: opinion comparisons of orthodontists, pediatric dentists, and general practitioners.J Orthod. 2002 Dec;29(4):287-91; discussion 277. doi: 10.1093/ortho/29.4.287. J Orthod. 2002. PMID: 12444269
-
A comparison of the reliability and validity of 3 occlusal indexes of orthodontic treatment need.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001 Sep;120(3):240-6. doi: 10.1067/mod.2001.116401. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001. PMID: 11552122 Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing Dental Care: A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence Applications Among Various Dental Specialties.Cureus. 2023 Oct 14;15(10):e47033. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47033. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37965397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in orthodontics: a scoping review.Prog Orthod. 2021 Jul 5;22(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40510-021-00361-9. Prog Orthod. 2021. PMID: 34219198 Free PMC article.
-
ORIENTATE: automated machine learning classifiers for oral health prediction and research.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jun 20;23(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03112-w. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37340367 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Clinical Decision Making under Uncertainty in Dentistry: A Scoping Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;13(6):1076. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061076. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980383 Free PMC article.
-
A family-centered orthodontic screening approach using a machine learning-based mobile application.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jan;19(1):186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 17. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 38303845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salzmann JA. Handicapping malocclusion assessment to establish treatment priority. Am J Orthod. 1968;54(10):749–765. - PubMed
-
- Brook PH, Shaw WC. The development of an index of orthodontic treatment priority. Eur J Orthod. 1989;11(3):309–320. - PubMed
-
- Richmond S, Shaw WC, Roberts CT, Andrews M. The PAR Index (Peer Assessment Rating): methods to determine outcome of orthodontic treatment in terms of improvement and standards. Eur J Orthod. 1992;14(3):180–187. - PubMed
-
- Gardner JW, Stewart WH. Orthodontic treatment priority index. Washington (DC): US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare; 1967.
-
- Summers CJ. The occlusal index: a system for identifying and scoring occlusal disorders. Am J Orthod. 1971;59(6):552–567. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

