Accuracy of Neck stiffness, Kernig, Brudzinski, and Jolt Accentuation of Headache Signs in Early Detection of Meningitis
- PMID: 29503833
- PMCID: PMC5827054
Accuracy of Neck stiffness, Kernig, Brudzinski, and Jolt Accentuation of Headache Signs in Early Detection of Meningitis
Abstract
Introduction: The diagnostic value of clinical signs in early diagnosis of meningitis has been evaluated but the existing results are contradicting. The present study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of Kernig, Brudzinski, neck stiffness, and Jolt Accentuation of Headache (JAH) signs in this regard.
Methods: In this diagnostic accuracy study, patients with suspected meningitis who were referred to the emergency department were examined regarding presence or absence of the mentioned clinical signs and screening performance characteristics of the signs were calculated. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis was used as the reference test.
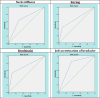
Results: 120 cases with mean age of 48.79 ± 21.68 years (18 - 93) were studied (63.3% male). Diagnosis of meningitis was confirmed for 45 (37.5%) cases. Neck stiffness (p < 0.001), Kernig (p < 0.001), Brudzinski (p < 0.001), and JAH (p < 0.001) had significantly higher frequency among patients with meningitis. The accuracy of neck stiffness, Kernig, Brudzinski, and JAH signs in early detection of meningitis were 0.676 (95% CI: 0.575-0.776), 0.667 (95% CI: 0.552-0.782), 0.720 (95% CI: 0.619-0.821), 0.749 (95% CI: 0.659-839), respectively.
Conclusions: It seems that diagnostic value of JAH is higher than other clinical signs but the accuracy of all signs is in poor to fair range. JAH had the highest sensitivity and Kernig and Brudzinski had the highest specificity.
Keywords: Meningitis; headache disorders; neurologic manifestations; physical examination; secondary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jolt accentuation of headache and other clinical signs: poor predictors of meningitis in adults.Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Jan;32(1):24-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2013.09.012. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Am J Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 24139448
-
Jolt accentuation and its value as a sign in diagnosis of meningitis in patients with fever and headache.Turk J Emerg Med. 2016 Nov 24;17(1):29-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tjem.2016.11.001. eCollection 2017 Mar. Turk J Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 28345071 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of jolt accentuation of headache cannot accurately rule out meningitis in adults.Am J Emerg Med. 2013 Nov;31(11):1601-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 24070978
-
[Sensitivity and specificity of clinical signs in adults].Med Mal Infect. 2009 Jul-Aug;39(7-8):445-51. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2009.06.015. Epub 2009 Jul 24. Med Mal Infect. 2009. PMID: 19632074 Review. French.
-
[Meningeal irritation].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2011;155(18):A2661. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2011. PMID: 21466719 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Sensitivity and specificity of meningeal signs in patients with meningitis.J Gen Fam Med. 2019 Jul 15;20(5):193-198. doi: 10.1002/jgf2.268. eCollection 2019 Sep. J Gen Fam Med. 2019. PMID: 31516806 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of jolt accentuation for headache in acute meningitis in the emergency setting.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 11;6(6):CD012824. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012824.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32524581 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA and purinergic processes modulate neck muscle activity evoked by noxious stimulation of dura.J Oral Pathol Med. 2020 Jul;49(6):547-554. doi: 10.1111/jop.13072. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Oral Pathol Med. 2020. PMID: 32531859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meurer WJ. Central Nervous System infections. In: Walls MH, editor. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine, Cocenpts and Clinical Practice. 8 ed. Sanders: Elsevier Inc; 2014. pp. 1447–59.
-
- Fitch MT, Beek D. Emergency diagnosis and treatment of adult meningitis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Waghhare S, Kalantri A, Joshi R, Kalantri S. Accuracy of physical signs for detecting meningitis: A hospital based diagnostic accuracy study. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 2010;112:752–7. - PubMed
-
- Durand ML, Calderwood SB, Weber DJ, Miller SI, Southwick FS, Caviness VS Jr, et al. Acute bacterial meningitis in adults: a review of 493 episodes. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:21–8. - PubMed
-
- Quagliarello VJ, Scheld WM. Treatment of bacterial meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:708–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources