Myoblast mitochondrial respiration is decreased in chronic binge alcohol administered simian immunodeficiency virus-infected antiretroviral-treated rhesus macaques
- PMID: 29504290
- PMCID: PMC5835494
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13625
Myoblast mitochondrial respiration is decreased in chronic binge alcohol administered simian immunodeficiency virus-infected antiretroviral-treated rhesus macaques
Abstract
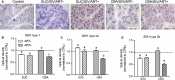
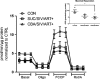
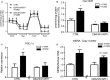
Work from our group demonstrated that chronic binge alcohol (CBA)-induces mitochondrial gene dysregulation at end-stage disease of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection in antiretroviral therapy (ART) naïve rhesus macaques. Alterations in gene expression can disrupt mitochondrial homeostasis and in turn contribute to the risk of metabolic comorbidities characterized by loss of skeletal muscle (SKM) functional mass that are associated with CBA, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, and prolonged ART. The aim of this study was to examine the interaction of CBA and ART on SKM fiber oxidative capacity and myoblast mitochondrial respiration in asymptomatic SIV-infected macaques. SKM biopsies were obtained and myoblasts isolated at baseline and 11 months post-SIV infection from CBA/SIV/ART+ and from sucrose (SUC)-treated SIV-infected (SUC/SIV/ART+) macaques. CBA and ART decreased succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity in type 1 and type 2b fibers as determined by immunohistochemistry. Myoblasts isolated from CBA/SIV/ART+ macaques showed decreased maximal oxygen consumption rate (OCR) compared to myoblasts from control macaques. Maximal OCR was significantly increased in control myoblasts following incubation with formoterol, a beta adrenergic agonist, and this was associated with increased PGC-1α expression and mtDNA quantity. Additionally, formoterol treatment of myoblasts isolated from CBA/SIV/ART+ macaques partially restored maximal OCR to levels not significantly different from control. These results show that CBA in combination with ART impairs myoblast mitochondrial homeostasis in SIV-infected macaques. Moreover, our findings suggest that adrenergic agonists can potentially ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction. Future studies will elucidate whether physical exercise in HIV patients with alcohol use disorder can improve mitochondrial health.
Keywords: Chronic alcohol; HIV; SIV; mitochondria.
© 2018 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicle miR-206 improves chronic binge alcohol-mediated decreased myoblast differentiation in SIV-infected female macaques.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):C1626-C1637. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00290.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39099419
-
Chronic Binge Alcohol-Induced Dysregulation of Mitochondrial-Related Genes in Skeletal Muscle of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques at End-Stage Disease.Alcohol Alcohol. 2017 May 1;52(3):298-304. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agw107. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017. PMID: 28069597 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic binge alcohol administration accentuates expression of pro-fibrotic and inflammatory genes in the skeletal muscle of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Nov;38(11):2697-706. doi: 10.1111/acer.12545. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25421506 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Impairs Bioenergetics and Differentiation Capacity of Myoblasts from Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Female Macaques.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 19;25(4):2448. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042448. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397125 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Alters Skeletal Muscle Bioenergetic Function: A Scoping Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 15;25(22):12280. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212280. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596345 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiological Consequences of At-Risk Alcohol Use; Implications for Comorbidity Risk in Persons Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 18;12:758230. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.758230. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35115952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal muscle bioenergetic health and function in people living with HIV: association with glucose tolerance and alcohol use.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Nov 1;321(5):R781-R790. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00197.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34585616 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic binge alcohol mediated hepatic metabolic adaptations in SIV-infected female rhesus macaques.Alcohol Alcohol. 2024 Jul 21;59(5):agae060. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agae060. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024. PMID: 39233472
-
Extracellular vesicle miR-206 improves chronic binge alcohol-mediated decreased myoblast differentiation in SIV-infected female macaques.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):C1626-C1637. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00290.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39099419
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: At the Nexus between Alcohol-Associated Immunometabolic Dysregulation and Tissue Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 12;24(10):8650. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108650. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bagby, G. J. , Zhang P., Purcell J. E., Didier P. J., and Nelson S.. 2006. Chronic binge ethanol consumption accelerates progression of simian immunodeficiency virus disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 30:1781–1790. - PubMed
-
- Bonet‐Ponce, L. , Saez‐Atienzar S., da Casa C., Flores‐Bellver M., Barcia J. M., Sancho‐Pelluz J., et al. 2015. On the mechanism underlying ethanol‐induced mitochondrial dynamic disruption and autophagy response. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1400–1409. - PubMed
-
- Carbonari, M. , Pesce A. M., Cibati M., Modica A., Dell'Anna L., D'Offizi G., et al. 1997. Death of bystander cells by a novel pathway involving early mitochondrial damage in human immunodeficiency virus‐related lymphadenopathy. Blood 90:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Cardellach, F. , Taraschi T. F., Ellingson J. S., Stubbs C. D., Rubin E., and Hoek J. B.. 1991. Maintenance of structural and functional characteristics of skeletal‐muscle mitochondria and sarcoplasmic‐reticular membranes after chronic ethanol treatment. Biochem. J. 274(Pt 2):565–573. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardellach, F. , Galofre J., Grau J. M., Casademont J., Hoek J. B., Rubin E., et al. 1992. Oxidative metabolism in muscle mitochondria from patients with chronic alcoholism. Ann. Neurol. 31:515–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

