In vitro antioxidant activity of phenolic-enriched extracts from Zhangping Narcissus tea cake and their inhibition on growth and metastatic capacity of 4T1 murine breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29504313
- PMCID: PMC5854635
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1700162
In vitro antioxidant activity of phenolic-enriched extracts from Zhangping Narcissus tea cake and their inhibition on growth and metastatic capacity of 4T1 murine breast cancer cells
Abstract
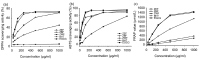
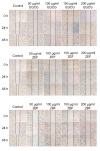
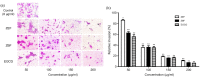
Phenolics, as the main bioactive compounds in tea, have been suggested to have potential in the prevention of various human diseases. However, little is known about phenolics and their bioactivity in Zhangping Narcissue tea cake which is considered the most special kind of oolong tea. To unveil its bioactivity, three phenolic-enriched extracts were obtained from Zhangping Narcissue tea cake using ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water. Their main chemical compositions and in vitro bioactivity were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). The ethyl acetate fraction (ZEF) consisted of higher content of phenolics, flavonoids, procyanidins, and catechin monomers (including epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), epicatechin gallate (ECG), and gallocatechin gallate (GCG)) than n-butanol fraction (ZBF) and water fraction (ZWF). ZEF exhibited the strongest antioxidant capacity in vitro due to its abundant bioactive compounds. This was validated by Pearson correlation and hierarchical clustering analyses. ZEF also showed a remarkable inhibition on the growth, migration, and invasion of 4T1 murine breast cancer cells.
Keywords: Oolong tea; Antioxidant activity; Metastasis; Cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chemical characterization and bioactivity of phenolics from Tieguanyin oolong tea.J Food Biochem. 2019 Jul;43(7):e12894. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12894. Epub 2019 May 15. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353716
-
Simultaneous determination of seven bioactive components in Oolong tea Camellia sinensis: quality control by chemical composition and HPLC fingerprints.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Jan 11;60(1):256-60. doi: 10.1021/jf204312w. Epub 2011 Dec 27. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22098505
-
Antioxidant properties of fractions and polyphenol constituents from green, oolong and black teas.Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1993 Apr;17(2):77-84. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1993. PMID: 7809277
-
Potential molecular targets of tea polyphenols in human tumor cells: significance in cancer prevention.In Vivo. 2002 Nov-Dec;16(6):397-403. In Vivo. 2002. PMID: 12494882 Review.
-
Statistical Approaches to Assess the Association between Phenolic Compounds and the in vitro Antioxidant Activity of Camellia sinensis and Ilex paraguariensis Teas.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(10):1456-73. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.750233. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015. PMID: 24918265 Review.
Cited by
-
Matcha Green Tea Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Inflammatory Responses.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 6;13(6):1950. doi: 10.3390/nu13061950. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34204055 Free PMC article.
-
Widely targeted metabolomics analysis of different Wuyi Shuixian teas and association with taste attributes.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 5;9(8):e18891. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18891. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37588613 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiles and potential antioxidant mechanisms of hawk tea.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 28;15(1):3600. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88160-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39875806 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Herbal Teas in Regulating Cellular Homeostasis and Autophagy and Their Implications in Regulating Overall Health.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 23;13(7):2162. doi: 10.3390/nu13072162. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34201882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Tea Powder on the Cooking Properties, Antioxidative Potential and Volatile Profiles of Dried Noodles.Foods. 2022 Mar 17;11(6):858. doi: 10.3390/foods11060858. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35327280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benzie IFF, Strain JJ. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999;299:15–27. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99005-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chavan U, Shahidi F, Naczk M. Extraction of condensed tannins from beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L.) as affected by different solvents. Food Chem. 2001;75(4):509–512. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00234-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

