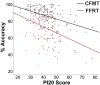
Adults have moderate-to-good insight into their face recognition ability: Further validation of the 20-item Prosopagnosia Index in a Portuguese sample
- PMID: 29504464
- PMCID: PMC6293437
- DOI: 10.1177/1747021818765652
Adults have moderate-to-good insight into their face recognition ability: Further validation of the 20-item Prosopagnosia Index in a Portuguese sample
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Duchaine B., Nakayama K. (2006). The Cambridge face memory test: Results for neurologically intact individuals and an investigation of its validity using inverted face stimuli and prosopagnosic participants. Neuropsychologia, 44, 576–585. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.07.001 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources