On-Column Dimethylation with Capillary Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Online Determination of Neuropeptides in Rat Brain Microdialysate
- PMID: 29504751
- PMCID: PMC6236683
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04965
On-Column Dimethylation with Capillary Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Online Determination of Neuropeptides in Rat Brain Microdialysate
Abstract
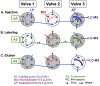
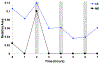
We have developed a method for online collection and quantitation of neuropeptides in rat brain microdialysates using on-column dimethylation with capillary liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (cLC-MS2). This method addresses a number of the challenges of quantifying neuropeptides with cLC-MS. It is also a completely automated and robust method for the preparation of stable isotope labeled-peptide internal standards to correct for matrix effects and thus ensure accurate quantitation. Originally developed for tissue-derived proteomics samples ( Raijmakers et al. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2008 , 7 , 1755 - 1762 ), the efficacy of on-column dimethylation for native peptides in microdialysate has not been demonstrated until now. We have modified the process to make it more amenable to the time scale of microdialysis sampling and to reduce the accumulation of nonvolatile contaminants on the column and, thus, loss of sensitivity. By decreasing labeling time, we have a temporal resolution of 1 h from sample loading to elution and our peptide detection limits are in the low pM range for 5 μL injections of microdialysate. We have demonstrated the effectiveness of this method by quantifying basal and potassium stimulated concentrations of the neuropeptides leu-enkephalin and met-enkephalin in the rat hippocampus. To our knowledge, this is the first report of quantitation of these peptides in the hippocampus using MS.
Figures


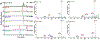
Similar articles
-
Rapid preconcentration for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry assay of trace level neuropeptides.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013 Nov;24(11):1700-9. doi: 10.1007/s13361-013-0605-1. Epub 2013 Apr 17. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23592077 Free PMC article.
-
Practical aspects of in vivo detection of neuropeptides by microdialysis coupled off-line to capillary LC with multistage MS.Anal Chem. 2009 Mar 15;81(6):2242-50. doi: 10.1021/ac802391b. Anal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19196160 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing adsorption to improve recovery and in vivo detection of neuropeptides by microdialysis with LC-MS.Anal Chem. 2015 Oct 6;87(19):9802-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02086. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26351736 Free PMC article.
-
The absolute quantification of endogenous levels of brain neuropeptides in vivo using LC-MS/MS.Bioanalysis. 2011 Jun;3(11):1271-85. doi: 10.4155/bio.11.91. Bioanalysis. 2011. PMID: 21649502 Review.
-
Challenges for the in vivo quantification of brain neuropeptides using microdialysis sampling and LC-MS.Bioanalysis. 2016 Sep;8(18):1965-85. doi: 10.4155/bio-2016-0119. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Bioanalysis. 2016. PMID: 27554986 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in isobaric labeling and applications in quantitative proteomics.Proteomics. 2022 Oct;22(19-20):e2100256. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202100256. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35687565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-Pot Extraction and Quantification Method for Bile Acids in the Rat Liver by Capillary Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 16;6(12):8588-8597. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00403. eCollection 2021 Mar 30. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33817519 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in mass spectrometry analysis of neuropeptides.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 Mar;42(2):706-750. doi: 10.1002/mas.21734. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 34558119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing mass spectrometry for the quantitative analysis of neuropeptides.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Jul;18(7):607-621. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.1967146. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34375152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and recent applications in omics investigations.Anal Methods. 2020 Sep 28;12(36):4404-4417. doi: 10.1039/d0ay01194k. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Anal Methods. 2020. PMID: 32901622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Piguet PN, The RA Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1993, 266, 1139–1146. - PubMed
-
- Yoshitake S; Ijiri S; Kehr J; Yoshitake T Neurochem. Int 2013, 62, 314–323. - PubMed
-
- Bodnar RJ Peptides 2014, 62, 67–136. - PubMed
-
- Ogren SO; Kuteeva E; Elvander-Tottie E; Hokfelt T Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 626, 9–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

