Programmed Sports Therapy (PST) in People with Haemophilia (PwH) "Sports Therapy Model for Rare Diseases"
- PMID: 29506547
- PMCID: PMC5836382
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0777-7
Programmed Sports Therapy (PST) in People with Haemophilia (PwH) "Sports Therapy Model for Rare Diseases"
Abstract
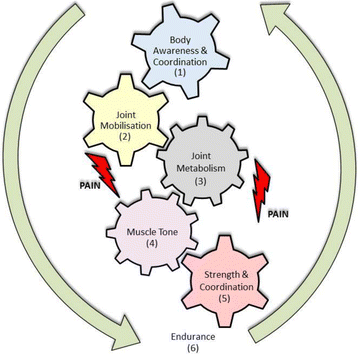
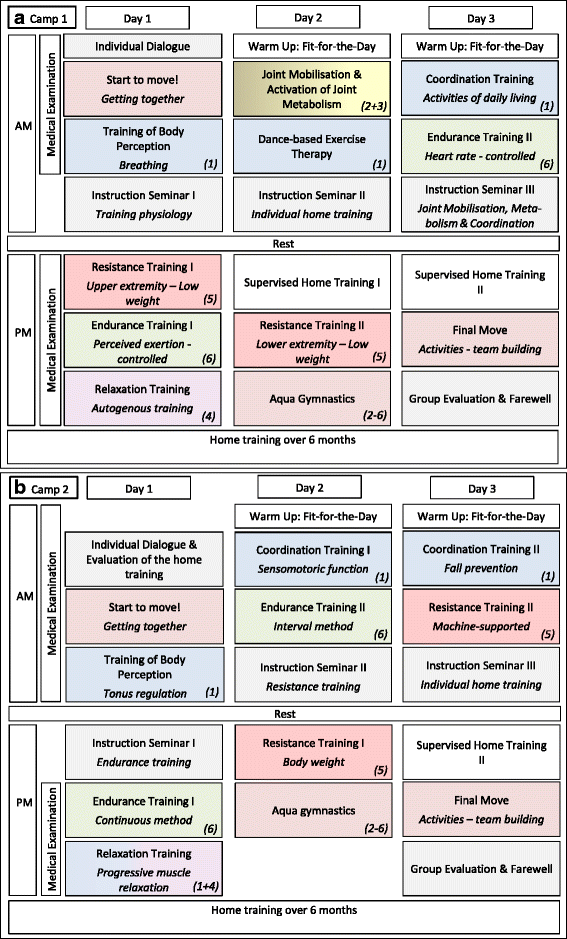
Sports and exercise therapy becomes more and more integrated in the treatment plan of different diseases. Although the benefits of this therapy are of high quality evidence, e.g. in cardiovascular diseases, no concepts of sports therapy are available as a treatment option for rare diseases.During the last eighteen years, we analyzed the situation as well as necessity, and developed a model, contents and the concept of the "Programmed Sports Therapy (PST)" for the treatment of PwH (people with haemophilia) as our model of rare disease. Many studies have shown that motoric skills are depressed in PwH, and that this gap to healthy people increases during age. The only way to reduce this progression is an appropriate therapy, adapted to the necessities of PwH. In haemophilia, in particular, physio- and sports therapy treatments should go hand in hand, the first in the acute phase after bleeding, the second later, after the acute phase has finished. One model, which considers all the different challenges, can be the cogwheel model presented here. Since haemophilia is a rare disease, new training concepts are necessary because classical group therapies are often impossible. PST based on the combination of sports therapy camps together with a supervised autonomous home training helps to directly bring the training to the trainee, in order to enhance key competences and improve the individual situation in PwH, and perhaps in patients with other rare diseases.The experience and scientific data substantiate the success of "Programmed Sports Therapy (PST)" and even this can be a model for other rare diseases.
Keywords: Coordination; Endurance; Exercise; Haemophilia; Physiotherapy; Prevention; Rare diseases; Rehabilitation; Sport; Strength.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Hilberg T. Physical activity in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Epidemiology and mechanisms. Hamostaseologie. 2008;28:9–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

