Efficacy and safety of electrical moxibustion for knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29506572
- PMCID: PMC5836464
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2514-x
Efficacy and safety of electrical moxibustion for knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a significant health issue because it causes pain and functional limitation. Many studies have reported that moxibustion, a treatment in traditional Korean medicine, is effective in treating KOA. However, conventional moxibustion produces smoke, harmful gases, and odors that can adversely affect the eyes, skin, and throat. It is also difficult to control the intensity of stimulation in conventional moxibustion. An electrical moxibustion device was developed to circumvent these problems, but there are few studies of that device. We will evaluate the efficacy and safety of electrical moxibustion as a treatment for KOA, and compare it with traditional indirect moxibustion and usual care.
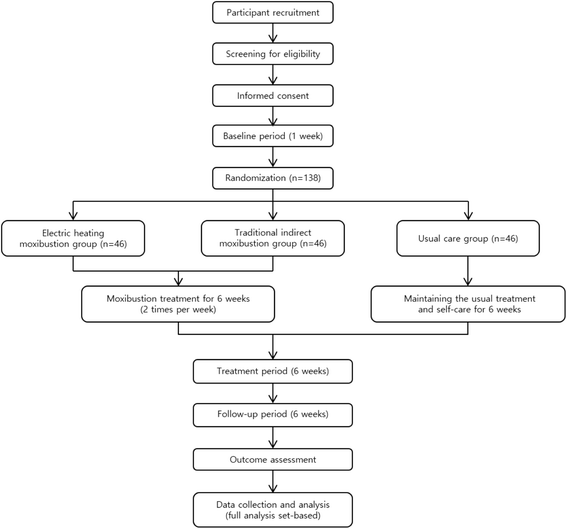
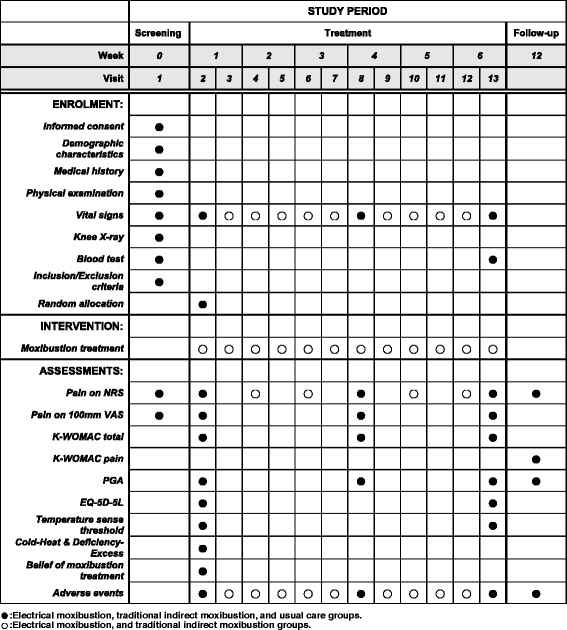
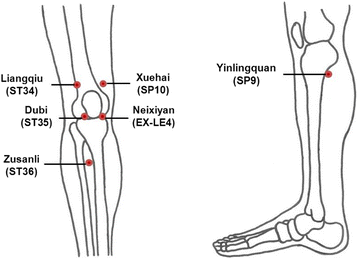
Methods: This is a multicenter, randomized, open, assessor-blinded, parallel-group clinical trial. A total of 138 eligible participants with KOA will be randomly allocated into three groups (electrical moxibustion, traditional indirect moxibustion, or usual care) with a 1:1:1 ratio. Participants in each moxibustion group will receive 12 sessions of moxibustion treatment at 6 acupoints (ST36, ST35, ST34, SP9, EX-LE4, SP10) plus up to 2 points of "ashi", if needed, over a period of 6 weeks (2 sessions per week). A specifically designed device that provides thermal stimulation using electrical energy will be used for the electrical moxibustion group. Participants in the usual care group will receive usual treatment and self-care. The primary outcome measure is change in pain on a numerical rating scale (NRS) from week 1 to week 6. The secondary outcome measures are pain assessed on a visual analog scale (VAS), the Korean version of the Western Ontario and McMaster osteoarthritis index (K-WOMAC), patient global assessment (PGA), and the European quality of life five dimension five level scale (EQ-5D-5 L). Safety will be assessed by monitoring adverse events at each visit. Follow-up measurements will be performed at 12 weeks after baseline measurements.
Discussion: This trial will provide evidence on the efficacy and safety of electrical moxibustion as a treatment for KOA.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03287570 . Registered on 19 September 2017.
Keywords: Electrical moxibustion; Knee osteoarthritis; Moxibustion; Randomized controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was written according to general ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and Korean Good Clinical Practice. The protocol was also approved by the Institutional Review Board of each trial center (protocol number 2017–0002, protocol version 3.1) and was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov. All participants will be informed of the methods of the trial, including potential benefits, possible adverse events, and personal responsibilities, and will then provide written informed consent.
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed the final manuscript, and consent for publication. There are no personal or private data contained in this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Yanhong C, Xiaobing S. Current status and progress on the epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis at home and abroad. Chin J Tradit Med Traumatol Orthop. 2012;20(6):81–84.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

