Mechanistic Role of the Calcium-Dependent Protease Calpain in the Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by MPO (Myeloperoxidase)
- PMID: 29507101
- PMCID: PMC6467284
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10305
Mechanistic Role of the Calcium-Dependent Protease Calpain in the Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by MPO (Myeloperoxidase)
Abstract
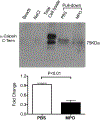
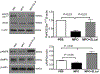
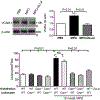
MPO (myeloperoxidase) is a peroxidase enzyme secreted by activated leukocytes that plays a pathogenic role in cardiovascular disease, mainly by initiating endothelial dysfunction. The molecular mechanisms of the endothelial damaging action of MPO remain though largely elusive. Calpain is a calcium-dependent protease expressed in the vascular wall. Activation of calpains has been implicated in inflammatory disorders of the vasculature. Using endothelial cells and genetically modified mice, this study identifies the µ-calpain isoform as novel downstream signaling target of MPO in endothelial dysfunction. Mouse lung microvascular endothelial cells were stimulated with 10 nmol/L MPO for 180 minutes. MPO denitrosylated µ-calpain C-terminus domain, and time dependently activated µ-calpain, but not the m-calpain isoform. MPO also reduced Thr172 AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) and Ser1177 eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) phosphorylation via upregulation of PP2A (protein phosphatase 2) expression. At the functional level, MPO increased endothelial VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1) abundance and the adhesion of leukocytes to the mouse aorta. In MPO-treated endothelial cells, pharmacological inhibition of calpain activity attenuated expression of VCAM-1 and PP2A, and restored Thr172 AMPK and Ser1177 eNOS phosphorylation. Compared with wild-type mice, µ-calpain deficient mice experienced reduced leukocyte adhesion to the aortic endothelium in response to MPO. Our data first establish a role for calpain in the endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation of MPO. The MPO/calpain/PP2A signaling pathway may provide novel pharmacological targets for the treatment of inflammatory vascular disorders.
Keywords: calpain; cell adhesion molecules; endothelial cells; inflammation; peroxidase.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

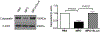

Comment in
-
Calpain: A Novel Mediator of MPO (Myeloperoxidase)-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction.Hypertension. 2018 Apr;71(4):574-576. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.10441. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 29507102 No abstract available.
References
-
- Haumer M, Amighi J, Exner M, Mlekusch W, Sabeti S, Schlager O, Schwarzinger I, Wagner O, Minar E and Schillinger M. Association of neutrophils and future cardiovascular events in patients with peripheral artery disease. Journal of vascular surgery. 2005;41:610–7. - PubMed
-
- Lee CD, Folsom AR, Nieto FJ, Chambless LE, Shahar E and Wolfe DA. White blood cell count and incidence of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke and mortality from cardiovascular disease in African-American and White men and women: atherosclerosis risk in communities study. American journal of epidemiology. 2001;154:758–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

