Dapagliflozin improves treatment satisfaction in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a patient reported outcome study (PRO study)
- PMID: 29507611
- PMCID: PMC5831584
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-018-0313-x
Dapagliflozin improves treatment satisfaction in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a patient reported outcome study (PRO study)
Abstract
Background: The benefits of sodium glucose cotransporters 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus include plasma glucose control, reduction in body weight and blood pressure, and low risk of hypoglycemia, although they may also cause genitourinary infections, polyuria, or volume depletion. It is not clear whether dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, improves treatment satisfaction among patients in a comprehensive way despite the negative side effects. This study assessed the effect of dapagliflozin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), body weight, and treatment satisfaction in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with oral hypoglycemic agents.
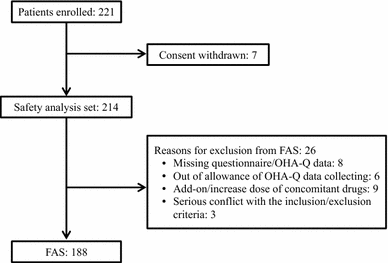
Methods: This multicenter, open-label, single-arm observational study included patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus administering dapagliflozin 5 or 10 mg per day for 14 weeks. Changes in treatment satisfaction were evaluated using a new version of the Oral Hypoglycemic Agent-Questionnaire (OHA-Q ver. 2) consisting of 23 items. Correlation between treatment satisfaction and HbA1c levels and body weight were analyzed using the Spearman's rank-correlation coefficient.
Results: Of the 221 patients enrolled, 188 completed the study. Mean HbA1c decreased from 7.8 ± 0.7% (62.1 ± 7.5 mmol/mol) to 7.3 ± 0.8% (55.9 ± 8.7 mmol/mol) (change - 0.6 ± 0.7%, P < 0.001) and body weight decreased from 82.5 ± 14.6 to 80.7 ± 14.8 kg (change - 2.3 ± 2.8 kg, P < 0.001). OHA-Q ver. 2 was validated as well, the mean OHA-Q ver. 2 total score increased from 44.3 ± 9.4 to 46.6 ± 9.8 (best score 69, worst score 0; change 2.3 ± 6.6, P < 0.001). The change in body weight significantly correlated with the OHA-Q ver. 2 total score (Spearman's ρ = - 0.17, P = 0.035). The change in HbA1c levels significantly correlated with the satisfaction subscale score (Spearman's ρ = - 0.19, P = 0.011).
Conclusions: Dapagliflozin significantly improved treatment satisfaction among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus for 14 weeks. Body weight loss significantly correlated with treatment satisfaction.Trial registration UMIN-CTR: UMIN000016304.
Keywords: Body weight; Dapagliflozin; Oral Hypoglycemic Agent-Questionnaire; Oral hypoglycemic agent; Patient reported outcome; Quality of life; SGLT2 inhibitors; Sodium glucose cotransporters 2 inhibitors; Treatment satisfaction; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Swallow R, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:147–158. doi: 10.1111/dom.12188. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources