Desmin- and vimentin-mediated hepatic stellate cell-targeting radiotracer 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI for liver fibrosis imaging with SPECT
- PMID: 29507624
- PMCID: PMC5835940
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.22806
Desmin- and vimentin-mediated hepatic stellate cell-targeting radiotracer 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI for liver fibrosis imaging with SPECT
Abstract
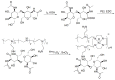
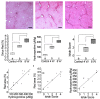
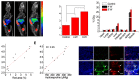
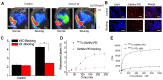
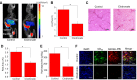
Extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation in liver fibrosis is caused by the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The goal of this study was to develop a 99mTc-labeled N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) that specifically interacts with desmin and vimentin expressed on activated HSCs to monitor the progression and prognosis of liver fibrosis using single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging. Methods: GlcNAc-conjugated polyethylenimine (PEI) was first prepared and radiolabeled with 99mTc. Noninvasive SPECT imaging with 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI was used to assess liver fibrosis in a carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) mouse model. The liver uptake value (LUV) of 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI was measured by drawing the region of interest (ROI) of the whole liver as previously suggested. The LUV of the CCl4 groups was compared with that of the olive oil group. Next, we estimated the correlation between the results of SPECT imaging and physiological indexes. After treatment with clodronate liposome, the LUV of 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI in fibrotic mice was compared with that in control mice. Results:99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI is a hydrophilic compound with high radiochemical purity (>98%) and good stability. It could specifically target desmin and vimentin on the surface of activated HSCs with high affinity (the Kd values were 53.75 ± 9.50 nM and 20.98 ± 3.56 nM, respectively). The LUV of 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI was significantly different between the CCl4 and control groups as early as 4 weeks of CCl4 administration (3.30 ± 0.160 vs 2.34 ± 0.114%/cc; P ˂ 0.05). There was a strong correlation between the LUV and Sirius Red quantification (R = 0.92, P ˂ 0.001). Compared with control, clodronate liposome treatment reduced the LUV of 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI (4.62 ± 0.352 vs 2.133 ± 0.414%/cc; P ˂ 0.05). Conclusion:99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI SPECT/CT was useful in assessing liver fibrosis and monitoring the treatment response.
Keywords: 99mTc-GlcNAc-PEI; SPECT imaging; desmin; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic stellate cells; vimentin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Guido M, Rugge M, Chemello L. et al. Liver stellate cells in chronic viral hepatitis: the effect of interferon therapy. J Hepatol. 1996;24:301–307. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis - from bench to bedside. J Hepatol. 2003;38:38–53. - PubMed
-
- Reeves HL, Burt AD, Wood SJ. et al. Hepatic stellate cell activation occurs in the absence of hepatitis in alcoholic liver disease and correlates with the severity of steatosis. J Hepatol. 1996;25:677–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

