Differentially expressed microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma invert effects of copy number aberrations of prognostic genes
- PMID: 29507679
- PMCID: PMC5823624
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24070
Differentially expressed microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma invert effects of copy number aberrations of prognostic genes
Abstract
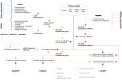
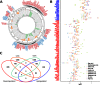
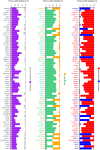
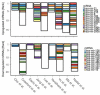
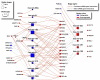
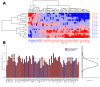
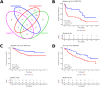
In many cancers, significantly down- or upregulated genes are found within chromosomal regions with DNA copy number alteration opposite to the expression changes. Generally, this paradox has been overlooked as noise, but can potentially be a consequence of interference of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms, including microRNA-mediated control of mRNA levels. To explore potential associations between microRNAs and paradoxes in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) we curated and analyzed lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) data, comprising gene expressions, copy number aberrations (CNAs) and microRNA expressions. We integrated data from 1,062 tumor samples and 241 normal lung samples, including newly-generated array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) data from 63 LUAD samples. We identified 85 "paradoxical" genes whose differential expression consistently contrasted with aberrations of their copy numbers. Paradoxical status of 70 out of 85 genes was validated on sample-wise basis using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) LUAD data. Of these, 41 genes are prognostic and form a clinically relevant signature, which we validated on three independent datasets. By meta-analysis of results from 9 LUAD microRNA expression studies we identified 24 consistently-deregulated microRNAs. Using TCGA-LUAD data we showed that deregulation of 19 of these microRNAs explains differential expression of the paradoxical genes. Our results show that deregulation of paradoxical genes is crucial in LUAD and their expression pattern is maintained epigenetically, defying gene copy number status.
Keywords: copy number aberrations; gene regulatory network; lung adenocarcinoma; microRNA; prognostic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Phillips JL, Hayward SW, Wang Y, Vasselli J, Pavlovich C, Padilla-Nash H, Pezullo JR, Ghadimi BM, Grossfeld GD, Rivera A, Linehan WM, Cunha GR, Ried T. The consequences of chromosomal aneuploidy on gene expression profiles in a cell line model for prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8143–9. - PubMed
-
- Hyman E, Kauraniemi P, Hautaniemi S, Wolf M, Mousses S, Rozenblum E, Ringnér M, Sauter G, Monni O, Elkahloun A, Kallioniemi OP, Kallioniemi A. Impact of DNA amplification on gene expression patterns in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6240–5. - PubMed
-
- Pollack JR, Sørlie T, Perou CM, Rees CA, Jeffrey SS, Lonning PE, Tibshirani R, Botstein D, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO. Microarray analysis reveals a major direct role of DNA copy number alteration in the transcriptional program of human breast tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99:12963–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Järvinen AK, Autio R, Haapa-Paananen S, Wolf M, Saarela M, Grenman R, Leivo I, Kallioniemi O, Mäkitie AA, Monni O. Identification of target genes in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by high-resolution copy number and gene expression microarray analyses. Oncogene. 2006;25:6997–7008. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

